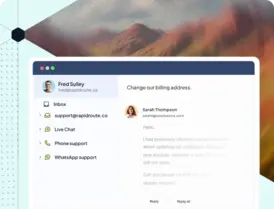
Customers don’t care if you’re on five platforms or ten; they care about not having to repeat themselves.
Yet, that’s exactly what most end up doing. 86% of customers expect conversations to move seamlessly across channels, yet few companies actually deliver that experience (Nextiva). Each time a customer repeats information, it signals that your systems aren’t connected.
That’s where omnichannel customer service comes in. It connects chat, email, phone, and WhatsApp into one continuous conversation. Agents see the full context, so they can pick up right where the customer left off.
In this guide, we’ll break down what omnichannel customer service really means, how it works in practice, and what steps you can take to make it work for your team.
Table of Contents
- What is omnichannel customer service?
- Omnichannel Service vs. Multichannel Service: What’s the Real Difference?
- What are the benefits of omnichannel customer service?
- What channels should your omnichannel customer support include?
- What makes omnichannel support actually work?
- How to build an omnichannel customer service strategy: Step-by-step guide
- Step 1. Map out your customer journey to spot breaks
- Step 2. Invest in a help desk that gives you central visibility
- Step 3. Fix your core channel right with clear ownership
- Step 4. Automate repetitive tasks to free up your team
- Step 5. Build channel-specific workflows
- Step 6. Track performance across all channels
- Real-world omnichannel customer service examples & use cases
- How to measure omnichannel customer service success?
- Best practices for omnichannel customer service
- The future of omnichannel support
- Fix your customer experience before adding new channels
- Frequently Asked Questions
What is omnichannel customer service?
Omnichannel customer service is when every interaction across chat, email, phone, social, or any other channel connects into a single, continuous customer conversation.
For support teams, that means full context in one view. If a customer messages on WhatsApp and follows up over email, the agent instantly sees the entire thread.
That context directly shapes experience and loyalty. 43% of consumers say they’d pay more for greater convenience, and 42% would pay more for a friendly, welcoming experience (PwC). Omnichannel support delivers fast, consistent, and personal service at every touchpoint.
As Tod Ellington, VP of Operations at Whitestone, put it on our Experience Matters podcast:
“When your systems are aligned, support stops feeling like a relay race. Everyone knows what’s happening, and customers feel it too.”
Omnichannel does exactly that. It keeps context moving with the customer, so every handoff feels seamless instead of like a reset.
Omnichannel Service vs. Multichannel Service: What’s the Real Difference?
Both models allow customers to reach you through various channels, including email, chat, phone, or social media, but only one actually connects them.
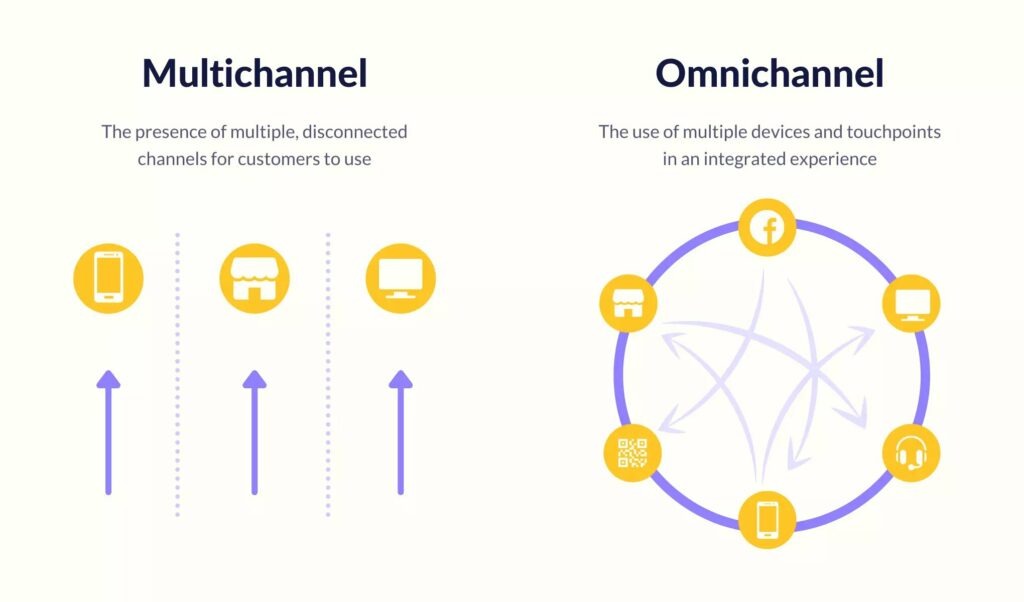
This is what it comes down to.
Multichannel Customer Service
Agents manage emails in one tab, chats in another, and calls in a separate tab. When a customer switches channels, the context doesn’t follow, which means agents have to ask for details again, and customers have to start over.
You can usually spot a multichannel setup if:
- Agents ask customers to repeat order numbers or previous issues.
- There’s no shared view of the customer’s past conversations.
- Reports show separate metrics for each channel instead of a single view.
Omnichannel Customer Service
Omnichannel customer support, on the other hand, stitches everything together. If a customer starts on chat and follows up by email, your agent sees the entire conversation. With access to the customer’s history, the customer service agent can provide faster, more efficient support across all channels.
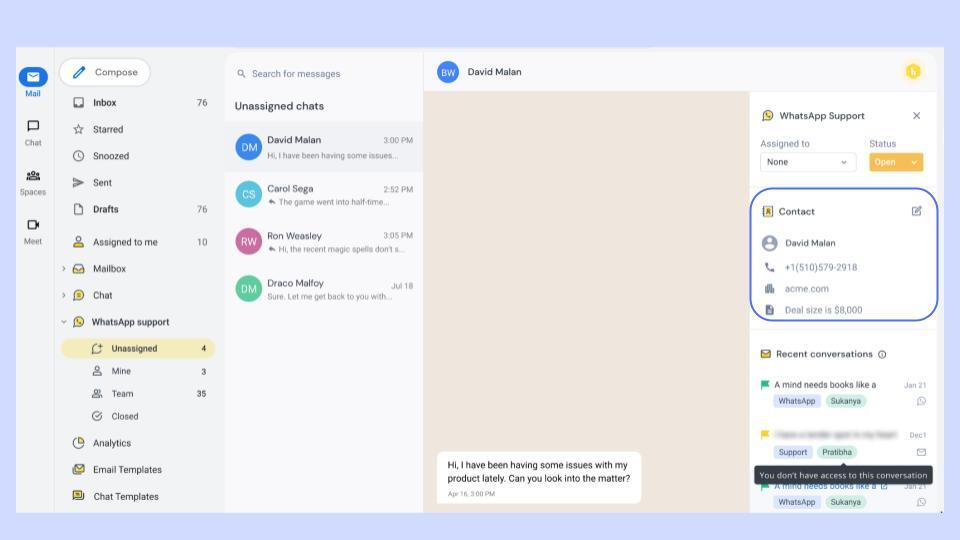
Customers never have to start from zero, and agents respond faster with complete visibility. That’s not a “bonus feature”; it’s the difference between building trust and driving churn.
Pro Tip: If your agents constantly ask, “Can you tell me what happened so far?” You’re likely stuck in a multichannel setup. A true omnichannel system gives them everything they need, upfront.
As Shep Hyken said on Episode 1 of the Experience Matters podcast:
“Ask yourself, is what I’m doing right now making things easier for the customer?”
Multichannel can make it harder. Omnichannel makes it effortless by supporting the entire customer journey.
Here’s a quick comparison between omnichannel services and multichannel services:
| Aspect | Multichannel | Omnichannel |
|---|---|---|
| Experience | Feels fragmented across platforms | Feels like one continuous conversation |
| Context | Lost when switching channels | Carries over seamlessly |
| Customer Effort | High — customers repeat themselves | Low — customers never start over |
| Agent View | Disjointed, multiple tools | Unified dashboard, full history |
| Impact | Slower resolutions, higher frustration | Faster support, higher satisfaction |
Recommended reading
What are the benefits of omnichannel customer service?
Omnichannel customer service is about connecting all customer interactions, like chat, email, phone, WhatsApp, and social media, into one shared system. When every channel talks to each other, context never gets lost, and both customers and teams spend less time catching up.
Companies that do this well retain up to 89% of their customers, compared to 33% for those that don’t. Here’s what that difference looks like in practice:
For customers
- Customers never have to repeat themselves: Every message, email, and call is stored in a unified thread. So when a customer switches from chat to email, the agent already knows what’s happened.
- Customers get faster answers: Agents don’t spend time piecing together the conversation. With the full history visible, they can act immediately.
- Customers deal with fewer mistakes: Nothing slips through the cracks when updates sync automatically. If a billing issue is solved on chat, that change reflects everywhere, without any duplicates.
For businesses
- Agents handle more with less effort: One workspace replaces multiple tools. Agents don’t need to switch tabs or forward tickets to share context. That alone cuts minutes off every response.
- Managers see what’s working and what’s stuck: A unified view shows how many requests are open, how long they’ve been waiting, and who’s handling them. Managers can fix bottlenecks before they turn into backlogs.
- Data highlights what to fix outside support: When all customer interactions sit in one place, trends are obvious, like order complaints after a new shipping partner or spikes in chat volume after an app update. Teams can route these issues to the right owners fast.
- Support costs go down naturally: No duplicate tickets, fewer follow-ups, and faster resolutions mean lower costs per issue, without needing to hire more agents or buy more software.
Omnichannel setups make that feedback visible, so teams can act on it instead of losing it in disconnected tools.
Recommended reading
What channels should your omnichannel customer support include?
You don’t need to be everywhere, just where your customers already are. The right mix depends on your audience and your team’s capacity to manage those channels well. Focus on the ones that make communication faster and more reliable for both sides.
Here are the most important customer channels to include in your omnichannel service strategy:
- Email: Use for detailed questions or issues that need clear documentation. It gives customers space to explain and creates a written record for follow-ups.
- Live Chat: Best for real-time support while customers are on your site or app. It helps resolve issues immediately and reduces ticket volume from small queries.
- Messaging Apps (WhatsApp, Facebook Messenger, etc.): Great for short, quick exchanges. Ideal for sending updates, confirming details, or answering simple questions without the formality of writing a complete email.
- Phone Support: Best for complex or high-emotion issues. Phone support is especially useful for escalations or when dealing with high-value customers.
- Social Media (Twitter, Instagram, Facebook, LinkedIn): Best for public mentions or complaints. Respond quickly to show you’re attentive, then move the conversation to a private channel for details.
- Self-Service (Help Center, FAQs, Community Forums): Best for repeatable, simple issues. A well-structured knowledge base lets customers help themselves.
What makes omnichannel support actually work?
Omnichannel support only works when three fundamentals are in place. Without them, you’re adding more tools to an already messy process.
- Connected tools: Support falls apart when agents jump between tabs just to reply to one customer. That’s when things get missed. Agents should be able to manage everything from the same place, without switching tools.
- Shared context: Customers don’t care who they’re talking to—they just expect you to know what happened. If your agents don’t have that information, replies get delayed or feel disconnected. Make sure your system shows a full conversation history, even if it started on chat and moved to email, so that any agent can pick it up smoothly.
- Team alignment: Even with the right tools, things break if everyone works differently. Some reply fast, others wait. Some escalate too quickly, others don’t. Set channel-specific response goals, define when to escalate, and review past conversations as a team. That’s how you keep responses consistent and handoffs clean.
Recommended reading
How to build an omnichannel customer service strategy: Step-by-step guide
Most teams mistake omnichannel for “being everywhere.” It’s not. It’s about adding only the channels your customers use and connecting them so conversations don’t restart. Done right, you cut repetition, speed up resolutions, and get clean visibility into what’s breaking.
Here’s a practical step-by-step strategy to build an omnichannel customer service system that actually works:
Step 1. Map out your customer journey to spot breaks
Most support teams jump straight to adding new customer service channels. But before expanding, you need to know how customers already move between the ones you have—and where the experience falls apart.
Start with real data. Pull the last 30–45 days of conversations across email, chat, phone, and messaging. Note three things:
- Where customers switch channels (e.g., chat → email, email → phone).
- When they repeat details (“I already shared my order number”).
- How long does it take from first contact to resolution?
These patterns show you where context is getting lost. Next, talk to your frontline team. Ask:
- “Which channels create the most back-and-forth?”
- “When do you have to look for missing information?”
- “Which cases jump between teams or tools?”
Agents will point you to the friction that data alone can’t explain. Now, map one complete customer journey. Pick a common issue, let’s say, a billing dispute, and sketch the path:
Chat → (agent can’t issue refund) → Email → (billing team) → Resolution
Mark where the switch happens, why it happens, and how long it takes.
Finish by listing your top three breakpoints and a quick fix for each. Example:
- Chat → Email (Refunds): add “Order ID” to chat form.
- Email → Phone (Login): reduce SLA on access issues.
- WhatsApp → Email (Attachments): enable file uploads in messaging.
This gives you a simple, factual view of where context breaks and what’s worth fixing first. Without it, any omnichannel setup will only make the same problems faster and louder.
Step 2. Invest in a help desk that gives you central visibility
Once you know where context breaks are, the next step is to bring everything into one system. Without a central workspace, every fix you make will still sit in silos.
A connected help desk should do four things:
- Connect every channel. Email, chat, WhatsApp, phone, and social DMs should function as one continuous system.
- Show full conversation history. Agents should instantly see past interactions, including who handled them and what was said, across all channels.
- Track ownership and accountability. Every query must have a clear owner, SLA, and reminders for follow-ups.
- Provide real performance data. You should be able to analyze volume, response times, and reopen rates by channel to decide where to improve next.
💡 Hiver unifies all support channels like email, chat, voice, WhatsApp, and more in a familiar, inbox-like interface. Teams get a single view of every customer interaction, clear accountability, and AI-driven insights that improve response speed and quality.
Step 3. Fix your core channel right with clear ownership
Once you’ve mapped the customer journey, focus on the channel customers use most, usually email or live chat. If it’s chaotic, adding more channels will only multiply the chaos.
To bring structure to this:
- Use round-robin or rule-based assignment to automatically route incoming queries. Every conversation should have one clear owner until it’s resolved.
- Standardize how tickets are tagged, escalated, and closed so everyone follows the same playbook.
- Monitor response time, resolution rate, and first-contact resolution to spot where delays happen and where training or automation can help.
- Have a team lead or weekly queue owner who keeps an eye on priorities and ensures accountability across agents.
Once this channel runs smoothly, expand one at a time, only when the team can handle the next channel with the same level of discipline.
Step 4. Automate repetitive tasks to free up your team
We’ve all been stuck in a chatbot loop that refuses to connect to a human, and it’s frustrating. That’s because too many teams use automation to replace empathy instead of reducing repetitive work.
How to use automation wisely:
- Keep a visible “Talk to an agent” option in every bot flow.
- Escalate complaints, refunds, or sensitive cases directly to a human.
- Review automation logs regularly. Too many escalations mean the bot isn’t useful; too few may mean it’s blocking customers.
Your goal should be to clear your agents’ time, not replace human support.
Step 5. Build channel-specific workflows
Different support channels demand different tones, response times, and workflows, and your internal processes should adapt accordingly.
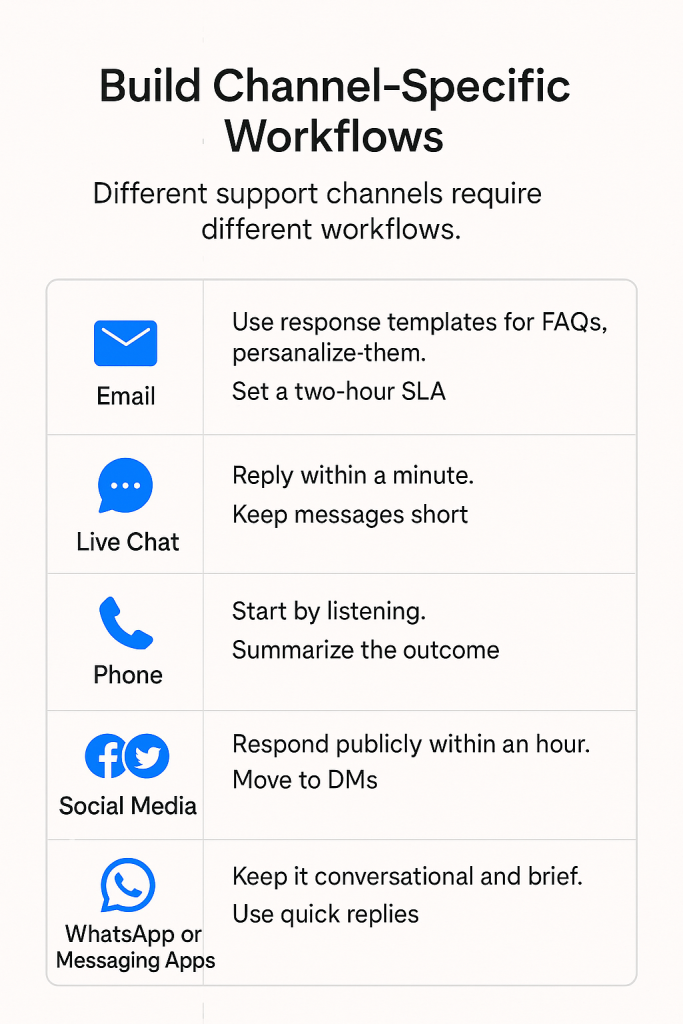
A slow, detailed response might work for email, but customers expect quick, clear answers on live chat or social media. Using the same playbook across all channels can lead to mismatched expectations and slower support.
To adapt according to the channel:
- Email: Use response templates for FAQs, but personalize them. For example: instead of “Your refund is being processed,” say “I’ve initiated your refund for Order #4781 — you’ll see it in your account within 3–5 days.” Set a two-hour SLA for first responses, include step-by-step instructions, and confirm resolution before closing the ticket.
- Live chat: Reply within a minute. Keep messages short, avoid jargon, and aim to resolve in one conversation. Limit agents to 2–3 chats at once for quality.
- Phone: Start by listening. Take quick notes and summarize the outcome before ending the call. Escalate urgent cases immediately in your help desk.
- Social media: Respond publicly within an hour. Acknowledge the issue, then move to DMs for details. Use a tone that’s friendly but professional.
- WhatsApp or messaging apps: Keep it conversational and brief. Use quick replies for common questions and automate order or status updates.
When your processes respect the strengths of each channel, customers get faster and more natural support. Also, your agents don’t have to fit everything into the playbook.
Step 6. Track performance across all channels
Omnichannel support only works when you measure what’s happening on each channel. Volume, response time, and satisfaction can vary wildly between email, chat, and social. Without analytics, you’re managing blind.
Here’s how to turn your data into decisions:
- Monitor channel-level metrics. Track first response time, resolution rate, and CSAT for every channel separately.
- Spot trends early. Use dashboards to see spikes in chat or email after a product update or campaign.
- Balance workloads. Reassign agents or adjust schedules when one channel gets overloaded.
- Refine SLAs. If response times consistently exceed goals on one channel, adjust targets or add capacity.
- Use insights for planning. Identify which channels drive the most volume or satisfaction and focus training or automation efforts there.
Regularly reviewing these insights keeps your support system healthy and helping your team stay ahead of demand.
💡For instance, Hiver’s reporting analytics allows you to drill down by channel, agent, or time period. This makes it easier to spot what’s working, what’s breaking, and where to act.
Real-world omnichannel customer service examples & use cases
It’s one thing to talk about omnichannel support in theory, but the real test is how it helps teams in the field. Here are a few examples of how companies used Hiver to connect their channels:
1. Golftini: Golf Apparel Brand
As Golftini, a women’s golf apparel brand, grew its online presence, so did the number of customer queries across sales, shipping, and returns. The team managed everything through Missive, but the system lacked clear ownership.
“Everyone had access to everything in Missive. That sounds great in theory, but it led to overlap, missed emails, and way too much time spent just figuring out who should do what,” Moe said.
Multiple agents often jumped into the same email, while others went unanswered; nearly 10–15% of customer queries were mishandled.
The team also spent 30–45 minutes every day triaging emails manually sorting them, deciding who should respond, and tagging teammates. Collision detection helped avoid duplicate replies but didn’t fix the core problem: there was no structured way to assign or track conversations.
Switching to Hiver changed that. The team brought email, chat, and WhatsApp into one central platform where:
- Queries were auto-assigned using round-robin rules, removing manual triage.
- Internal notes and @mentions made collaboration quick and visible.
- Automation rules filtered out ERP alerts and system-generated emails, reducing clutter.
The results were immediate:
- Email triage time dropped by 80%, saving over 70 hours a month.
- Response times improved by 60%, since every query had a clear owner.
- Non-actionable emails reduced by 65%, helping the team focus on what truly mattered.
With Hiver, Golftini gained complete visibility and accountability across channels. This helped the team stay organized and customers get faster, more consistent responses.
2. Fishburners: Australian Start-up Community
Fishburners, is a community for startups in Australia, handling questions about onboarding, memberships, invoices, events, and more.
Initially, the team used a mix of personal and shared inboxes, which led to broken handoffs, lost messages, and confusion about who owned a request.
Team members often emailed queries directly to one person, who then had to forward it. If that person was away, no one else could pick up the conversation and replies stalled. Because multiple inboxes were in play, the team missed tracking some messages entirely.
After implementing Hiver, everything landed in one shared system. Emails were tagged and auto-assigned. Internal notes and @mentions replaced forwards so the context stayed with the ticket. Even when someone was away, others could access the full history and continue the conversation.
The results were clear:
- 25 hours saved each month by eliminating manual triage and follow-ups.
- Zero missed messages across channels.
- Faster responses and clearer ownership without adding extra headcount.
For members, this meant an experience where switching between email and chat didn’t require repeating themselves and every reply felt consistent.
3. Airbnb: Online marketplace for lodging and vacation rentals
As Airbnb scaled globally, one of its biggest challenges was keeping teams connected across regions and time zones. Customer interactions, community operations, and business data all lived in separate tools, making it hard for teams to share insights or respond quickly to issues.
To fix this, Airbnb adopted Salesforce Sales Cloud and Slack to create a more connected, data-driven support system.
- Slack became the common workspace where regional teams could collaborate in real time. Support, operations, and engineering teams shared updates, escalated urgent issues, and solved guest concerns together, without relying on long email threads or delayed reports.
- Sales Cloud gave managers visibility into performance data, customer trends, and regional operations, all in one place.
- Tableau dashboards allowed teams to visualize patterns in customer needs and prioritize action faster.
The shift helped Airbnb’s teams move from siloed updates to instant collaboration and data-backed decisions. They could spot issues early, share learnings quickly, and deliver more consistent experiences to guests and hosts worldwide.
For customers, this meant smoother service like faster follow-ups, fewer disconnects, and a team that always had the context to help.
Across Golftini, Fishburners, and Airbnb, one thing stands out, connected systems create better service. When teams have full visibility and shared ownership, response times drop, handoffs get smoother, and customer trust grows.
How to measure omnichannel customer service success?
Tracking the right numbers like CSAT, First Response Time, and more makes the difference between omnichannel in theory and omnichannel that actually works.
| Metric | How to Measure | What to Do |
|---|---|---|
| First Response Time | Track per channel (chat under 1 min, email within 2 hrs). | If targets are missed, adjust SLAs or shift agents where demand spikes. |
| Resolution Time | Measure time from first contact to full closure. | Review channel handoffs and cut steps causing delays. |
| Customer Satisfaction (CSAT) | Run a 1-question survey after resolution on every channel. | Use low scores to spot and fix process or training gaps. |
| Channel Switch Rate | Tag tickets that span multiple channels. | If customers leave chat for email/calls, improve the first channel’s capability. |
| Agent Workload Balance | Track ticket distribution per agent and per channel. | Use round-robin assignment or automate routing to prevent overload. |
| Retention & Churn | Compare churn before vs. after omnichannel rollout. | If numbers don’t improve, revisit workflows to ensure support feels seamless. |
Here’s what to measure and what to do with it:
- First Response Time: Measure per channel (chat under a minute, email within two hours). If you’re missing targets, adjust SLAs or shift agents where demand spikes.
- Resolution Time: Track time from first contact to closure. If there are long delays, review handoffs between channels and cut unnecessary steps.
- Customer Satisfaction (CSAT): Run a one-question survey after resolution. Low scores on a specific channel signal process or training gaps you need to fix.
- Channel Switch Rate: Tag tickets that span multiple channels. If customers keep leaving chat for email or calls, improve the first channel’s ability to solve issues.
- Agent Workload Balance: Watch ticket distribution across agents. If some are overloaded, set up a round-robin assignment or automate routing.
- Retention and Churn: Compare churn before and after omnichannel rollout. If numbers don’t move, revisit whether your support is actually seamless.
Use these data points to rebalance teams, tighten processes, and prove that omnichannel is improving both speed and accuracy.
Best practices for omnichannel customer service
Omnichannel service fails when it’s treated as a checklist of channels. The companies who get it right treat it as an operating system. Here’s how to do the same:
1. Start with one channel, get it right. Pick the channel most customers use and fix it first. Make sure every query has an owner, response times are tracked, and nothing slips through before adding more channels.
2. Show agents the full conversation. A “real” omnichannel system shows the entire conversation across chat, email, WhatsApp, or phone in one view. If your agents are still asking “Can you tell me what happened so far?”, you’re not there yet.
3. Automate small tasks. Use AI triage and automation rules to route tickets and categorize requests for routine cases like order confirmations or password resets. But if the issue involves money, emotion, or cancellations, let a human take over.
4. Set clear response times for each channel. Live chat should get replies in under a minute, emails within a couple of hours, and social media within a day. Tell customers what to expect.`
5. Check how each channel is doing. If chat volumes spike after a product launch, temporarily move agents there to keep response times stable. If a channel stays quiet for weeks, pause it until you can staff it properly.
6. Teach agents how to handle on every channel. Train your team to change their tone and pace depending on the channel. Chat should be quick and friendly, email can be more detailed, and phone calls should focus on empathy.
7. Ask for feedback after every interaction. Send short CES or CSAT surveys automatically once a ticket is closed. Use those insights to compare performance across channels. If one consistently scores lower, that’s your next improvement target.
The future of omnichannel support
AI is reshaping customer support by speeding up responses, cutting routine work, and giving agents more time for complex issues.
Here are four emerging trends that are shaping the future of omnichannel support:
- AI assistants for agents: AI tools like Hiver’s Copilot draft replies, surface context, and learn from past interactions so agents respond faster and more accurately. AI Insights highlights trends such as rising ticket volume or slow replies, helping managers act before performance drops.
- Predictive, not reactive support: AI can now flag issues before customers report them, spotting repeated errors or sudden spikes in requests. It lets teams fix problems early, prevent backlogs, and deliver proactive help instead of reactive apologies.
- Knowledge that updates itself: AI-powered search brings the right answers from help docs and past cases in seconds. Keep content updated and embed knowledge tools directly in the workspace so agents don’t lose time switching tabs.
The future isn’t about replacing agents. It’s about giving them sharper tools and better visibility to handle every channel efficiently.
Fix your customer experience before adding new channels
When was the last time you reached out to customer support? You probably didn’t care whether it was email, chat, or a phone call. You just wanted a quick, accurate answer without repeating yourself.
That’s the real purpose of omnichannel: every interaction should feel like part of the same conversation.
To get there, here’s what to do:
- Map your customer journey and fix the breakpoints.
- Get your busiest channel running smoothly before adding more.
- Automate repetitive tasks, but keep humans for sensitive issues.
- Track performance channel by channel, and refine constantly.
The right tools make this easier. If you’re setting up omnichannel support and want something that simplifies your team’s day-to-day, try Hiver. It brings email, chat, WhatsApp, phone, and SMS together in one intuitive, inbox-like interface, so your team has everything in one place.
Plus, Hiver’s AI capabilities help agents work faster. It summarizes long threads, drafts contextual replies, and surfaces key details instantly.
Try Hiver for free and see how effortless connected support can be.
Frequently Asked Questions
1: What is omnichannel customer service?
It’s when all your support channels connect so customers never repeat themselves. To start, bring your busiest two channels into one system before adding more.
2: What are the 4 C’s of omnichannel?
Consistency, Convenience, Context, and Continuity. Use them as a checklist: are your replies consistent, easy to reach, carrying context, and flowing smoothly?
3: What is an example of omnichannel customer service?
A customer starts on chat, follows up by email, and later calls — and the agent sees the full history. Test this yourself by moving across two channels and checking if your system keeps context.
4: What is the difference between omnichannel and multichannel?
Multichannel = many channels, no connection. Omnichannel = channels linked together. If your agents ask, “Can you tell me what happened so far?”, you’re stuck in multichannel.
5: What is an omnichannel contact center?
It’s a single hub where agents handle every channel with context in one view. If your team is toggling tabs, you need to centralize.
6: How do you implement omnichannel customer service?
Map where customers switch channels, fix your main channel first, unify tools, set SLAs by channel, and automate simple tasks. Roll out one channel at a time.
7: What are the benefits of omnichannel customer service?
Faster replies, fewer repeated questions, happier customers, and higher retention. Start tracking CSAT and resolution time by channel to see the impact.
Start using Hiver today
- Collaborate with ease
- Manage high email volume
- Leverage AI for stellar service
 Skip to content
Skip to content