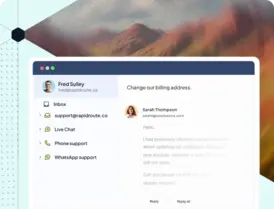
Most users don’t want to read long help articles when they’re trying to complete a task or fix an issue. They want to see exactly what to click and copy the steps. That’s why a video knowledge base works.
Short, screen-based videos make workflows easier to follow, reduce confusion, and help users finish tasks faster. In fact, over 75% of consumers prefer video over text when learning about a product or service.
A video knowledge base brings this clarity to your help center with searchable, visual guides users can watch, pause, and replay anytime. In this guide, you’ll learn how to create, organize, and maintain a video knowledge base that customers actually use—and that reduces support tickets.
Table of Contents
- How to Create a User-Friendly Video Knowledge Base
- Tip 1: Choose the Right Tool to Create the Video
- Tip 2: Clear Visual Cues
- Tip 3: Closed Captions
- Tip 4: Timestamps for Sections
- Tip 5: Convert Video to Interactive or Downloadable Text
- Tip 6: Variable Playback Speed
- Tip 7: Multi-Language Support for Sections in Video
- Tip 8: Make It Mobile-Friendly
- Tip 9: Host Your Video Knowledge Base
- Tip 10: Plug Videos Into Your Support Workflow (so agents don’t keep typing the same answer)
- How to Maintain Your Video Knowledge Base
- Best Practices for Creating A Video Knowledge Base
- Get Started with a Video Knowledge Base Today
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
TL;DR
A video knowledge base is a set of short help videos that show customers exactly what to do, step by step.
- Where it falls short: Videos go out of date after product changes. If you don’t review them, customers follow old steps and contact support anyway.
- Who it helps: Support teams dealing with repeat setup, login, billing, and “how do I” questions.
- Why it matters: Fewer repeat tickets and faster resolutions. Less back-and-forth for agents.
- What to do: Keep videos short. Add captions and timestamps. Highlight key clicks. Embed videos in help articles and share them in replies.
How to Create a User-Friendly Video Knowledge Base
To create a video knowledge base that actually reduces support tickets, focus on clarity, accessibility, and discoverability. Keep videos short, add captions and timestamps, optimize for mobile, and make sure videos appear exactly where customers ask for help.
Here are 10 tips to help you get started:
Tip 1: Choose the Right Tool to Create the Video
The Problem:
People overthink this step and either (a) buy a complex tool they don’t use, or (b) pick something too basic and end up re-recording everything. You don’t need a studio. You need a setup that helps you record clearly, edit fast, and publish without drama.
Examples:
- You record a walkthrough, but the cursor is impossible to follow, and users still get stuck.
- You make one mistake in the middle, and now you’re re-recording the whole thing.
- You avoid making videos at all because filming yourself feels awkward or time-consuming.
Why It’s a Big Deal:
Your tool choice decides whether video creation becomes a quick habit or a monthly “we should do this” project that never happens. The right stack saves time, keeps quality consistent, and helps your support team ship videos without needing a specialist.
Solution:
Pick a toolset that covers three basics: screen recording + simple editing + decent audio. Add AI video tools only if they help you publish faster.
Here’s how to choose:
1) Screen recording (for walkthroughs)
Look for tools that let you record screen + voice together, show the cursor clearly, and export in common formats. Loom, Screencastify, ScreenFlow, and Camtasia are common picks for product demos and step-by-step guides.
2) Basic editing (so you don’t re-record everything)
Make sure you can trim mistakes, cut dead air, add annotations, and use zoom/highlights for key clicks. Many screen recorders include this, which is usually enough when you’re starting out.
3) Audio (because bad audio ruins good videos)
A “decent microphone” matters more than fancy visuals. Even a basic USB mic can make your videos sound clear.
4) AI video tools (only if they save you time)
Tools like Synthesia, WowTo, Guidde, and Trupeer can help with things like scripts, voiceovers, or polished outputs when you don’t want to be on camera. Use them when speed and consistency matter more than a human face on screen.
Tip 2: Clear Visual Cues
The Problem:
Sometimes in videos, key points can easily be missed without visual cues to guide the viewer’s attention. This is especially true for complex or detailed subjects where the viewer needs to focus on specific elements.
Examples:
- In a software tutorial, a visual cue can highlight where to click to access a particular feature.
- During a product demo, arrows or circles can emphasize the product’s key features.
- In a troubleshooting video, color-coded text can indicate steps, warnings, and tips.
Why It’s a Big Deal:
Visual cues remove guesswork. They can help break down complex information into digestible chunks and emphasize key points that shouldn’t be missed. This means fewer rewinds and fewer “where do I click?” tickets.
Solution: Incorporate Clear and Effective Visual Cues
Here’s how you go about it:
Types of Visual Cues
Use a variety of visual cues such as arrows, circles, highlights, and zoom effects to guide the viewer’s attention. Choose the type of visual cue based on the content. For instance, use arrows for directional cues and highlights for emphasizing text or numbers.
Timing and Synchronization
Ensure that visual cues appear at the precise moment they are relevant. For example, an arrow should appear just as the narrator mentions the button to be clicked. Use editing software that allows you to synchronize visual cues with the audio or script. Test multiple times to ensure perfect timing.
Color and Contrast
Use colors that stand out against the background but are not too jarring. The goal is to attract attention without distracting from the overall content. Keep accessibility in mind by choosing colors that are distinguishable by those with color vision deficiencies.
Recommended reading
How to Create Great Knowledge Base Articles: Tips & Templates
Tip 3: Closed Captions
The Problem:
Without captions, customers who can’t use audio (or have hearing issues) can’t follow the steps. Captions also help when someone isn’t a native speaker or when the audio isn’t perfect. Moreover, you miss out on the opportunity to enhance comprehension and engagement for all viewers, regardless of their hearing ability or language proficiency.
Examples:
- A user who is deaf can fully understand a technical tutorial thanks to accurate closed captions.
- A viewer can use closed captions if they forgot their headset and avoid disturbing others around them with the volume.
- A non-native English speaker can better understand industry jargon through reading captions.
Why It’s a Big Deal:
Closed captions are not just an accessibility feature; they’re a tool that can enhance comprehension and extend the reach of your content to a global audience.
Solution: Implement High-Quality Closed Captions
Here’s how you go about it:
Accurate Transcription
Ensure that the captions are a verbatim representation of the spoken words, including important nuances and technical terms. Consider using specialized transcription services for content that includes industry jargon or complex terminology.
Real-Time Synchronization
The captions should appear in real-time as the words are spoken, without any noticeable lag. Use time-coding to ensure that captions are perfectly synchronized with the audio, enhancing the viewer’s understanding and engagement.
User Customization
Allow users to customize the appearance of captions, including font, size, and color, to suit their viewing preferences. Offer a preview option so users can see how their customization choices will appear during playback.
Inclusion of Non-Spoken Elements
Include descriptions of relevant non-spoken audio elements, such as [laughter], [applause], or [background music]. Use square brackets or another distinct visual method to differentiate these descriptions from spoken content.
Recommended reading
Tip 4: Timestamps for Sections
The Problem:
Support videos often cover multiple steps, but customers usually need just one part. Without timestamps for sections, users are forced to manually scrub through the video, which can be time-consuming and frustrating. This lack of easy navigation can lead to lower engagement and a subpar user experience.
Examples:
- A 20-minute tutorial video covers installation, basic features, and advanced settings. Without timestamps, a user wanting to know only about advanced settings has to skim through the entire video.
- A product FAQ video addresses multiple questions, but a viewer interested in just one question has no way to jump directly to that section.
- A troubleshooting video covers five different issues. A user experiencing only one of those issues has to waste time watching unrelated content.
Why It’s a Big Deal:
Timestamps act as a “table of contents” for your video, allowing users to jump directly to the content that’s most relevant to them. This enhances user satisfaction and makes your video content more accessible and user-friendly.
Solution: Implement Timestamps for Sections
Clearly Defined Sections
Break down your video into logical sections or chapters, each covering a specific topic or step. Use on-screen text or visual cues to indicate the start of a new section, making it easier for users to follow along.
Clickable Timestamps
Provide clickable timestamps in the video description that allow users to jump directly to different sections. Test the timestamps to ensure they lead to the exact starting point of each section, not a few seconds before or after.
On-Screen Timestamps
Display the timestamps on the video timeline, allowing users to hover over them to see what each section covers. Make sure these on-screen timestamps are easily visible but not intrusive, so they don’t distract from the video content.
User Engagement
Use analytics to track how often users are clicking on timestamps, which can provide insights into what sections are most relevant to your audience. Regularly tweak the timestamps if the video content is updated or expanded, ensuring they remain accurate and useful.
Tip 5: Convert Video to Interactive or Downloadable Text
The Problem:
Videos explain workflows best, but a text version makes them easier to reference, search, and revisit. Together, they help users get answers faster. Having a text option matters, especially when customers can’t (or don’t want to) rely on video.
Examples:
- A user is in a noisy airport who can’t hear the video well, even with headphones.
- Another user is on a limited data plan and doesn’t want to use up their data on a video.
- Some users may have learning preferences that make text-based information easier to absorb and review later.
Why It’s a Big Deal:
Flexibility is key in user experience. Offering multiple ways to consume the same content not only increases accessibility but also enhances user satisfaction. It shows that you’re considerate of varying user needs, which can lead to higher engagement and loyalty.
Solution: Offer a Convert-to-Text Feature with Interactive Highlights
Here’s how you go about it:
Text Conversion
Implement a feature that allows the entire video to be converted into a text-based format, or alternatively, use a text-to-video AI tool to enhance user engagement. This could be a downloadable document or a webpage that the user can refer to.
Use advanced speech-to-text algorithms to ensure the transcription is accurate. Offer the option to view this text alongside the video for a multi-modal learning experience.
Interactive Highlights
As the video progresses, the corresponding section of the text is highlighted in real-time. This allows users to follow along with the video or quickly locate specific sections in the text.
The highlighting should be smooth and well-timed with the video’s audio. Consider using color-coding or other visual cues to indicate different types of content, such as instructions, explanations, or key points.
Downloadable Format
Allow users to download the text in various formats, such as PDF, Word, or plain text. This enables them to read offline or even print the material for future reference.
Include any charts, graphs, or other visual aids from the video as supplementary material in the text document. Make sure these are also accessible and well-labeled.
User Control
Make this feature optional and easily toggled on or off. Not every user will want or need a text version, so it should be easy to switch between formats.
💡Pro Tip: Use this quick guide to decide when a video helps more than text (and when it doesn’t).
| Use video when… | Use text when… |
|---|---|
| The steps are visual (customers need to see where to click). | Customers need to scan quickly or jump to one step. |
| The process has multiple steps and small UI details. | The steps are simple and don’t need a screen walkthrough. |
| You’re showing a workflow, setup, or troubleshooting flow. | Customers need to copy/paste values, links, or commands. |
| You want to reduce “where do I find this?” questions. | Customers may be offline or have limited data. |
Tip 6: Variable Playback Speed
The Problem:
Not every user has the same learning pace or time constraints. Some may need to slow down the video to absorb complex information, while others may want to speed it up to quickly get to the point they’re interested in.
Examples:
- A user who’s new to the subject matter may need to slow down the video to fully grasp the concepts being discussed.
- An experienced user should speed through familiar content to get to the specific information they’re seeking.
- Some users may want to review content at a faster speed as a form of revision.
Why It’s a Big Deal:
Customization enhances user experience. By giving users control over the playback speed, you’re allowing them to consume content in a way that suits their individual needs, which can lead to better understanding and retention.
Solution: Implement Variable Playback Speed
Range of Speed Options
Offer a range of speeds, from 0.5x for those who need more time to absorb the content, up to 2x for those who want to skim through. Make sure the audio quality remains clear at all speeds. Test different speed options to ensure that both the video and audio synchronize well.
Easy-to-Find Controls
Place the speed control button in an easily accessible location on the video player interface, such as next to the volume or settings controls. Use intuitive icons or labels like a turtle for slower speeds and a hare for faster speeds to make the feature self-explanatory.
Save User Preferences
Allow the platform to remember a user’s preferred playback speed for future videos, making the experience more seamless. Give users the option to set different default speeds for different types of content, such as tutorials, overviews, or deep dives.
Tip 7: Multi-Language Support for Sections in Video
The Problem:
If your videos are only in one language, some customers won’t be able to follow the steps. They’ll get stuck, give up, and reach out to support instead.
Examples:
- A Spanish-speaking user wants to learn about a specific feature covered in your English-only video tutorial. Without multi-language support, they may struggle to understand the content or abandon the video altogether.
- A Japanese customer is interested in troubleshooting steps for a product. If the video sections are not available in Japanese, they may have to rely on inaccurate auto-translations or seek information elsewhere.
- A French-speaking user wants to jump to a specific section in a long FAQ video. Without French-language timestamps, they have to manually scrub through the video, leading to a frustrating experience.
Why It’s a Big Deal:
Multi-language support for sections not only makes your video knowledge base more accessible but also broadens its appeal to a global audience. This can lead to increased user engagement, customer loyalty, and potential market growth.
Solution: Implement Multi-Language Support for Sections
Here’s how to go about it:
Accurate Translations
Ensure that each section and its corresponding timestamp are accurately translated into multiple languages. Use translation tools (most video knowledge base tools, such as Trupeer and Wowto, have this feature) for linguistic and cultural accuracy. Avoid relying solely on automated translation tools, which can be imprecise.
User-Friendly Language Selection
Provide an intuitive language selection menu that allows users to easily switch between different languages for both the video and its sections. Place the language selection menu in a prominent, easily accessible location, such as near the video controls or at the top of the description.
Localized User Interface
In addition to translating the video sections, also localize the user interface elements like buttons, tooltips, and menus. Ensure that the localized interface is fully functional and provides the same user experience as the original language.
Cultural Sensitivity
Be aware of cultural nuances and sensitivities when translating content. What works in one language or culture may not be appropriate in another. Consult with cultural experts or native speakers to ensure that your translations are not only linguistically accurate but also culturally appropriate.
Tip 8: Make It Mobile-Friendly
The Problem:
We live in a mobile-first world, yet many video knowledge bases seem stuck in the desktop era. Lack of mobile responsiveness can make navigating the knowledge base on a smartphone or tablet a frustrating experience.
Examples:
- Videos that don’t adjust to fit the mobile screen require users to scroll horizontally.
- Text that’s too small to read on a mobile device, making users pinch and zoom constantly.
- Buttons or links that are too close together make it difficult to tap the right one.
Why It’s a Big Deal:
A significant portion of users will access your knowledge base via mobile devices. If the mobile experience is poor, you risk alienating a large part of your audience. This can result in an increase in support tickets and a decrease in customer satisfaction.
Solution: Make It Mobile-Friendly
Here’s how you go about it:
Responsive Design
Adopt a responsive design framework that automatically adjusts the layout based on the device’s screen size. This ensures that whether a user is on a smartphone, tablet, or desktop, the content scales appropriately. Use media queries in your CSS to fine-tune the experience for different screen sizes.
Readable Text
Opt for a legible font and a minimum font size of 16 pixels for body text to ensure that users can read without squinting or zooming.
Touch-Friendly Buttons
Increase the size of buttons and ensure adequate spacing between clickable elements to prevent misclicks. Use visual cues like color contrast or shadows to make buttons more noticeable.
Test Extensively
Don’t just assume your video knowledge base will work on mobile. Check it on real phones (iOS + Android) and different browsers. Use Lighthouse in Chrome DevTools or PageSpeed Insights to catch layout and speed issues, then do quick user testing focused on support tasks like playing the video, turning captions on, and using timestamps.
Tip 9: Host Your Video Knowledge Base
The Problem:
You can create great help videos and still end up with the same repeat tickets if customers can’t find the video, access it, or watch it without friction. If a video loads slowly, is difficult to access, or isn’t searchable, customers drop off and contact support anyway. Good hosting helps videos load fast and play smoothly, so customers have a better experience.
Examples:
- Customers find the video on YouTube… then get distracted and disappear.
- You’ve got 40 videos, but customers can’t search them, so they still email support.
- Videos load slowly in some regions, and people drop off.
Why It’s a Big Deal:
Hosting affects three things: discoverability (can people find it?), control (can you manage branding and access?), and speed (does it load fast?).
Solution:
Choose a hosting option based on what you need most: reach, control, organization, or full ownership.
Here’s how each option works:
1) YouTube (public or unlisted)
YouTube is a public website where people watch and share videos. It is free, fast, and familiar to most users. It has strong SEO potential, making your videos discoverable on Google, and sharing is incredibly easy.
2) Professional video hosting (Wistia, Vimeo, SproutVideo)
Professional video hosting tools, such as Wistia, Vimeo, and SproutVideo, are paid services designed for creating and hosting videos. They give you a clean, branded player, detailed analytics, and more control over how and where your videos appear on your site.
3) Dedicated video knowledge base tools (WowTo, Screendesk, Trupeer)
A dedicated video knowledge base platform like WowTo or Trupeer is a software built specifically to store, organize, and show help videos for product education and support. They include built-in search and categorization, AI-generated transcripts, and integrations with help desks and CRM systems. Some platforms also allow teams to convert MP4 to SCORM, making it easier to upload video-based training content into LMS platforms and track learner progress.
4) Self-hosted on your site (with a CDN)
In a self-hosted setup, you store the video files on your own servers and deliver them through a content delivery network (CDN). A CDN is a group of servers around the world that work together to load your videos faster for users in different regions.
Recommended reading
Tip 10: Plug Videos Into Your Support Workflow (so agents don’t keep typing the same answer)
The Problem:
Your videos can be solid and still not save your team time if they’re not connected to how customers ask for help. Customers will email, start a chat, or get stuck inside the product. If your videos aren’t part of those workflows, agents end up re-explaining things, and customers bounce between channels.
Examples:
- A customer emails a “how do I…” question, and the agent rewrites the same steps again.
- A chat turns into a long back-and-forth because the user can’t see what to click.
- A user is stuck inside a feature and opens a ticket because the help is not available right there.
- Your article has text steps, but the video isn’t embedded, so customers miss the faster path.
Why It’s a Big Deal:
This is where videos actually cut support load. When agents can share a video in seconds, you reduce handle time and follow-ups. When customers can help themselves with the product, fewer of them contact support in the first place.
Solution:
Make videos usable in three places: agent replies, your product UI, and your help articles. Then set up simple navigation that matches how your support team thinks.
Here’s how to do it:
- Let support agents share videos in responses. Connect your video library to your help desk so agents can paste links in a few clicks. For example, in Hiver, agents can quickly search for the right video and drop the link into an email or chat reply. It is much easier to say “Here is a quick video that walks you through it” than type out the same 10 steps.”
- Surface videos inside your product. Use in-app widgets, tooltips, or “Need help?” buttons that open relevant videos right next to the feature. This helps users without forcing them to leave the page.
- Embed videos within your knowledge base articles. Don’t keep text and video separate. Add a relevant video at the top of each article, allowing users to choose how they prefer to learn. Customer service tools, such as Intercom and Hiver, make this easy by letting you add a YouTube link (or any video URL) directly into an article. The video appears above the written steps, providing customers with a clear walkthrough, and your support team can share a single link that covers everything.
Why having a knowledge base isn’t enough (you have to maintain it)
A knowledge base isn’t a “set it and forget it” project. The moment your product, pricing, policy, or UI changes, parts of your help content become wrong. Then customers follow outdated steps, get stuck, and contact support anyway. Worst part: they trust your docs less the next time.
When you don’t maintain it, simple stuff breaks fast: screenshots and labels don’t match what customers see, steps don’t fit the current flow, and edge cases get ignored. Policies go out of date too (refunds, SLAs, onboarding, security), and search starts pointing people to the wrong page because titles and keywords weren’t updated.
How to Maintain Your Video Knowledge Base
To maintain a video knowledge base, regularly update videos when your product changes. Also, archive outdated content, use AI tools to automate updates, and track analytics to see which videos need refreshing.
Having said that, maintaining a video knowledge base is not easy, but with the right approach, maintenance becomes manageable. Here are some tips to help you:

1. Update Videos As Per Product Changes
Set up a process to catch these changes early. When your product team ships a big change, ask a few simple questions:
- Which videos show this part of the interface?
- Are any of these steps now incorrect or unclear?
- Can we patch the video, or do we need a full re-record?
Sometimes you only need to re-record 30 seconds that show a new UI and then stitch it into the existing video. Use AI voiceover tools like Synthesia or WowTo to regenerate just that section without touching the original recording.
2. Use AI to Automate Updates and Localization
AI can save you a lot of time. It can help you:
- Speed up script creation: You generate first-draft scripts from prompts, existing help articles, or product change logs.
- Localize at scale: AI translation and dubbing tools, such as Synthesia, HeyGen, or Rask AI, can automatically create captions and voiceovers in multiple languages. This is essential if you serve a global audience and want to offer customer support in their native language.
- Enhance audio quality automatically. AI-powered audio cleanup tools, such as Descript or Adobe Podcast, remove background noise, balance levels, and polish recordings.
3. Monitor Analytics and Update Based on User Behavior
Analytics reveal patterns you’d miss otherwise. They show which videos solve real problems and which ones confuse or bore viewers. They can also help expose gaps like topics your customers are searching for but you haven’t covered yet.
- Use analytics tools to track performance: If you’re hosting your videos on YouTube, use YouTube Analytics to track views, watch time, and drop-off points. If you use a dedicated video knowledge base tool like WowTo or Screendesk, their built-in dashboards make it easy to see which videos people watch, skip, or abandon halfway.
- Use your customer service tools to spot content gaps: Modern customer service tools come with analytics that can show you which topics still create a lot of tickets. That’s a sign that those topics need a clearer explanation or a different format, such as a short video.
For example, in Hiver, reports and analytics make it easy to see these patterns and decide what to fix or record next. - Add visible timestamps to build trust: Display “last updated” dates on your videos. This signals to users that your content is actively maintained and reliable.
4. Set review cycles and clear ownership
Not all videos will need the same level of attention. Create tiered review cycles based on relevance and importance.
Set up a review schedule based on traffic and criticality:
- High-traffic, critical videos (onboarding, billing, core features): review monthly or quarterly
- Medium-traffic videos: review every 6 months
- Low-traffic or niche videos: review annually
Assign content ownership for accountability. Give specific team members responsibility for sections of your video knowledge base. When someone “owns” the onboarding videos or troubleshooting guides, updates happen faster, and nothing slips through the cracks.
Archive or retire outdated content. Do not keep outdated content around. Archive or retire videos that no longer align with the product, and redirect users to the updated versions.
Best Practices for Creating A Video Knowledge Base
Creating a good video knowledge base is about making videos easy to find, watch, and understand for everyone. Here are some tips to help you:
- Be strategic about what to turn into a video. Support videos take longer to create and update than text. So don’t make a video for every question. Create videos when the process has many small steps, users need to see the screen to understand it, and the feature won’t change soon.
- Don’t neglect captions. Captions matter because many people watch with sound off, and some customers have hearing impairments. Clear, time-synced captions help them follow each step without guessing.
- Keep videos short. Aim for one task per video, ideally 1–2 minutes. If it’s longer, split it into separate videos (setup, common errors, next steps).
- Write a quick script before you record. Even a few bullet points keep the video focused and reduce re-recording. You can also reuse the script as the text version in your help center.
- Show the result early. Tell viewers what they’ll finish by the end of the video so they know they’re in the right place.
- Plan for updates. Review videos after product releases, and check the videos linked to your top ticket topics regularly so steps and screenshots don’t go out of date.
- Make videos easy for support agents to share. Use clear titles (“How to…”, “Fix…”, “Set up…”), add a one-line summary, and keep the links consistent so agents can drop the right video into replies fast.
Get Started with a Video Knowledge Base Today
A video knowledge base reduces friction for both customers and your team. Customers get quick, visual answers without hunting through articles or waiting for support. Your team spends less time repeating explanations and more time on high-value work.
Treat your video library as an evolving resource. Each new clip, updated script, and improved flow builds momentum over time. Start small, launch with confidence, and let the library grow into an essential part of your customer experience.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is a video knowledge base?
A video knowledge base is a collection of organized, searchable videos like tutorials, how-to guides, and FAQs that help customers learn about your product without reading long help docs. It typically includes screen recordings, walkthroughs, and troubleshooting videos hosted on your website or help center.
2. What are the best Video knowledge base platforms?
Popular video knowledge base tools include WowTo, Synthesia, Guidde, and Trupeer. The right one depends on whether you need basic screen recording, AI help for scripts and voiceover, or a full library with search, categories, and integrations. Compare features like captions, analytics, and your help desk integration before you pick.
3. How often should I update Knowledge Base Videos?
Update any video as soon as the UI, steps, pricing, or policy changes. For ongoing reviews, check high-traffic videos monthly or quarterly, medium-traffic every six months, and low-traffic annually. Use support ticket trends and drop-off data to prioritize.
 Skip to content
Skip to content