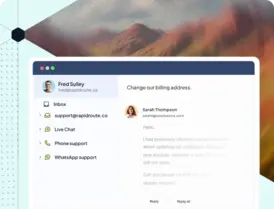
People expect answers instantly, whether they are customers trying to fix an issue or employees looking for information. They want clear, self-serve guidance without waiting for a response.
When those answers are scattered across documents, emails, or tools, everything slows down. Teams repeat the same explanations, customers get frustrated, and simple tasks take far longer than they should.
A knowledge base solves this by putting all your important information in one organized, searchable place. It helps customers troubleshoot on their own and gives employees a reliable source of truth for everyday work.
Before you build a new knowledge base or improve the one you have, it helps to understand what it is, how it works, and why it matters. In this article, we walk you through the essentials of a knowledge base in a simple, practical way.
Table of Contents
- What Is a Knowledge Base?
- What Is the Use of a Knowledge Base?
- How Does a Knowledge Base Work?
- What Are the Types of Knowledge Bases?
- What Does a Good Knowledge Base Include?
- How to Create a Knowledge Base (Step-by-Step)
- Step 1: Identify Your Audience
- Step 2: Collect Questions and Existing Documentation
- Step 3: Choose the Right Knowledge Base Software
- Step 4: Create Categories
- Step 5: Write Articles (With Templates)
- Step 6: Optimize for Search & SEO
- Step 7: Add Visuals, Videos, Step-by-Step Guides
- Step 8: Publish, Gather Feedback
- Step 9: Maintain & Update Regularly
- Knowledge Base Best Practices
- How Different Teams Use a Knowledge Base
- What to Look for in a Knowledge Base Platform
- The Future of Knowledge Bases
- Frequently Asked Questions
What Is a Knowledge Base?
A knowledge base is a single, searchable place where you store useful information like FAQs, how-to guides, troubleshooting steps, and product details.
It can be used externally by customers for self-service support or internally by employees who need quick access to policies, training materials, and best practices.
Knowledge bases exist because organizations generate huge amounts of information every day. Without a structured way to store and access that knowledge, teams waste time searching for answers, customers wait longer for help, and everyday work starts to slow down.
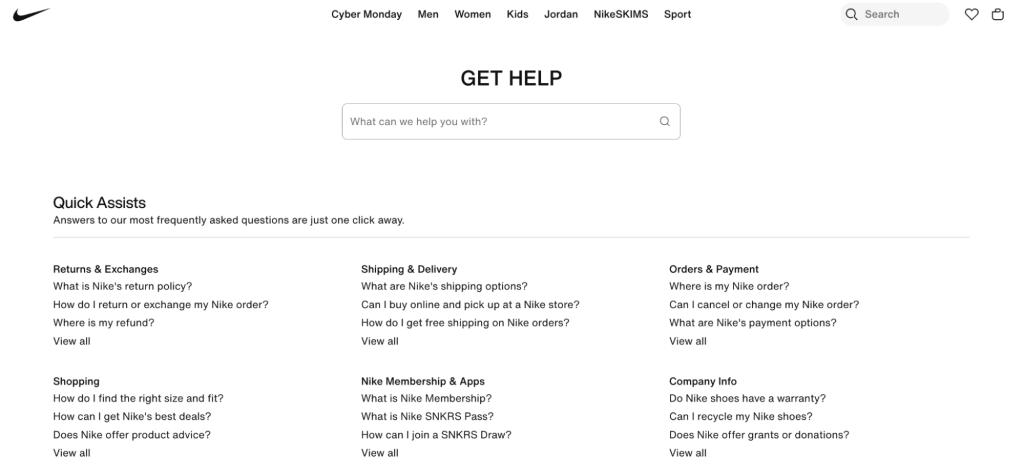
For example, the global sportswear brand, Nike, maintains a well-organized knowledge base where FAQs are grouped under a “Quick Assists” section to make navigation easy. Users can search for answers directly and, if needed, move to a clear Contact Us section with phone, chat, and support options.
What Is the Use of a Knowledge Base?
A knowledge base helps your team and your customers find answers quickly without relying on someone else. It improves support efficiency, reduces unnecessary back-and-forth, and keeps information flowing smoothly across your organization.
Here’s what that looks like in practice:
Provide Instant Answers, 24/7
Customers and employees get help the moment they need it. A searchable library removes wait times and keeps problem-solving fast even outside business hours.
Reduce Repetitive Queries for Support Teams
Clear articles and troubleshooting steps deflect routine questions before they hit the queue. Your team spends more time on high-value conversations instead of repeating the same explanations.
Keep Information Consistent Across Teams
A centralized repository removes scattered docs and conflicting answers. Everyone relies on the same verified content, which improves collaboration and reduces errors.
Improve Onboarding and Training
New hires pick up systems and processes faster because they have structured, self-paced documentation. It reduces interruptions and shortens the time it takes for someone to become productive.
Capture Organizational Knowledge
A well-documented knowledge base prevents expertise from disappearing when employees leave or switch roles. The information your team depends on stays accessible and easy to reference.
How Does a Knowledge Base Work?
To get the most value from a knowledge base, you need a clear sense of how it works. Here’s a quick look at how it operates:
- Store information in structured articles: Teams write clear, focused articles that answer common questions or explain specific tasks. Each article follows a consistent format with titles, steps, visuals, and links.
- Organize content using categories and tags: Categories group related topics (like “Billing” or “Setup”), while tags connect articles across categories for easier discovery.
- Index all content for quick search: The system indexes article titles, body text, tags, and metadata so users can instantly retrieve relevant results.
- Use AI to power smarter search results: Modern knowledge bases apply AI to understand user intent, suggest relevant articles, and deliver faster, more accurate results.
- Surface instant answers through auto-suggestions: As users type, the system recommends matching articles or highlights key content, reducing the time to resolution.
What Are the Types of Knowledge Bases?
Knowledge bases are built for different audiences and use cases. You may need one for your customers, one for your employees, or an AI-driven system that automates how information is searched and delivered.
Here are the three most common types of knowledge bases:
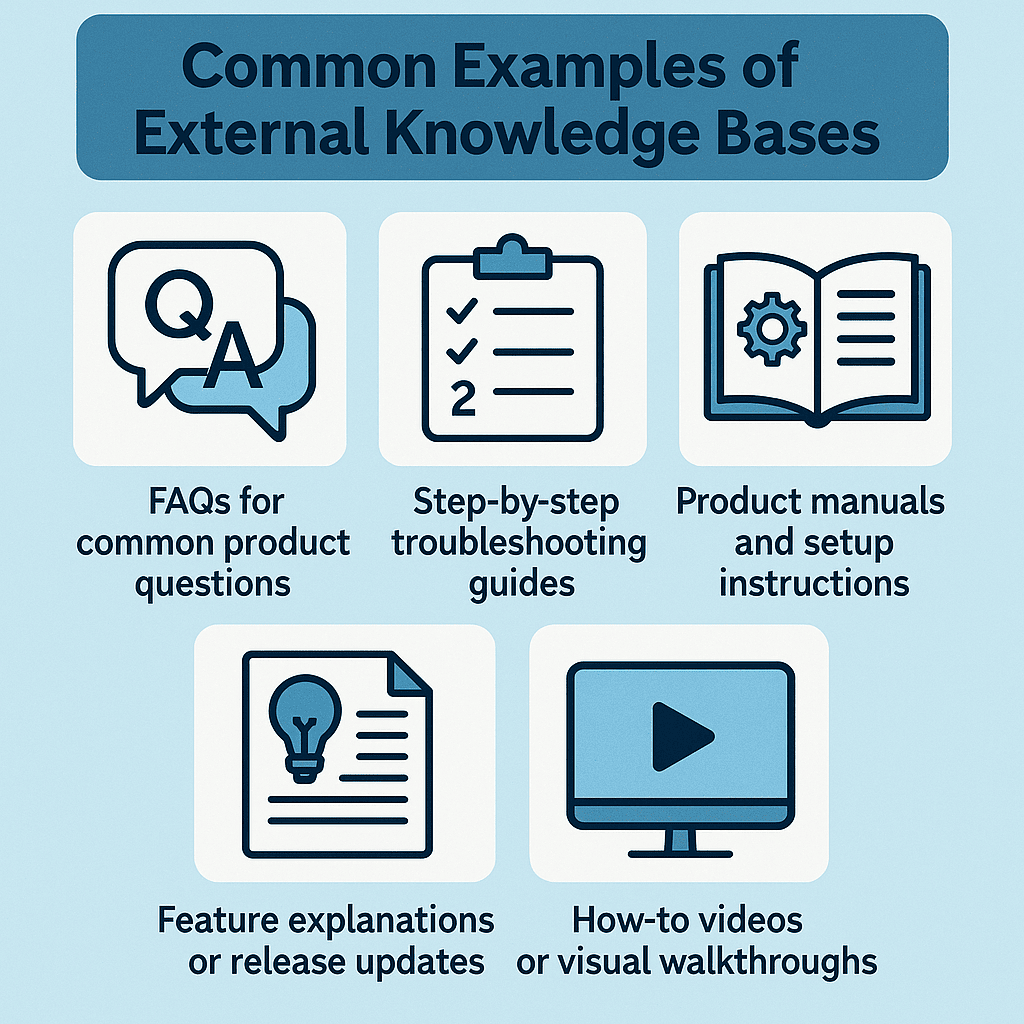
1. External Knowledge Bases (Customer-Facing)
An external knowledge base helps your customers solve problems on their own. You give users a simple way to find answers without raising a ticket or waiting for an agent. These libraries often focus on self-service and reducing support load.
2. Internal Knowledge Bases (Employee-Facing)
An internal knowledge base helps your teams work faster and stay aligned. You centralize important information so employees do not have to see through email threads, Slack messages, or old documents.
An internal knowledge base reduces back-and-forth and makes it easier for teams to collaborate.

Recommended reading
Internal KB or External KB – What to Choose and How to Choose?
3. AI Knowledge Bases
AI knowledge bases are becoming the new standard because they go beyond static articles. You give users a system that understands queries, pulls the right answers instantly, and adapts based on past behavior.
How AI knowledge bases work:
- Automate search by understanding natural language queries
- Recommend articles automatically based on context
- Retrieve answers faster using vector search and embeddings
- Flag outdated content that needs revision
- Suggest new articles based on trending queries
You deliver a smarter, more personalized knowledge experience. Users get accurate answers in seconds, and your support team benefits from automated suggestions during ticket resolution.
Recommended reading:
Some companies now maintain video-based knowledge bases to explain workflows or product features more clearly, especially for teams that learn better visually.
If you’re exploring this approach, a well-structured video knowledge base can make complex steps much easier to follow.
What Does a Good Knowledge Base Include?
A strong knowledge base gives people quick, reliable answers by keeping information organized, easy to read, and continually updated.
- Logical Structure: Helps users navigate smoothly through clear categories and well-grouped topics.
- Concise, Easy-to-Read Articles: Saves time by explaining tasks and fixes in simple, skimmable steps.
- Robust Search Functionality: Guides users to the right answer instantly using keywords, filters, and smart suggestions.
- Troubleshooting Guides: Walk users through common issues so they can solve problems without raising a ticket.
- Regular Updates: Keeps information accurate and relevant as products, policies, or workflows evolve.
- Audience-Focused Content: Matches the needs of your users to improve clarity and usefulness.
- Feedback Tools (“Was this helpful?”): Shows which articles need improvement and captures gaps in documentation.
- Visual Aids: Uses screenshots, diagrams, or short videos to make instructions easier to follow.
- User Permissions & Controls: Ensures the right teams can create, edit, or access content safely.
How to Create a Knowledge Base (Step-by-Step)
A clear process keeps knowledge base creation organized, predictable, and easy for any team to execute. Here’s a step-by-step guide to building a knowledge base:
Step 1: Identify Your Audience
A clear picture of who will use the knowledge base shapes tone, structure, and depth. Support patterns often reveal whether users need beginner-friendly guides or advanced explanations.
Pro Tip: Scan recent tickets or internal chats to see how users naturally describe problems.
Step 2: Collect Questions and Existing Documentation
A content inventory highlights what information already exists and where gaps remain. Teams usually uncover duplicate answers or outdated docs during this step.
Pro Tip: Pull the last 90 days of tickets and cluster them to identify high-volume themes instantly.
Step 3: Choose the Right Knowledge Base Software
Tools with strong search, permissions, templates, and analytics simplify long-term maintenance. AI-powered platforms also help users surface answers automatically.
Step 4: Create Categories
Logical grouping reduces friction and helps users navigate easily. Clear category names also guide authors on where new articles belong.
For example, SaaS teams often use groups like “Getting Started,” “Billing,” “Troubleshooting,” and “Integrations.”
Recommended reading
Step 5: Write Articles (With Templates)
A predictable article structure improves readability and reduces time spent rewriting content later. Writers avoid confusion because every piece follows the same flow.
Step 6: Optimize for Search & SEO
Clear titles, keywords, links, and metadata help both readers and search engines understand the content. Clean URLs also play a quiet role in performance.
Step 7: Add Visuals, Videos, Step-by-Step Guides
Screenshots, diagrams, videos, and GIFs remove ambiguity from setup steps and troubleshooting flows. Visual cues also reduce repetitive “where do I click?” questions.
For example, GIF-based onboarding guides often cut ticket volume noticeably for new product users.
Step 8: Publish, Gather Feedback
Real user feedback exposes unclear sections faster than internal reviews can. Early opinions from agents or employees help prevent confusion at scale.
Pro Tip: Add a “Was this helpful?” button to identify problem articles without manual surveys.
Step 9: Maintain & Update Regularly
Scheduled reviews keep information accurate as products, policies, or processes evolve. Analytics help pinpoint articles that drop in engagement or show spikes in failed searches.
If you want a deeper breakdown of each step, the complete guide on how to create a knowledge base walks through the same process in detail.
Knowledge Base Best Practices
You set up a knowledge base to simplify answers, so every article should be simple and easy to navigate. These best practices help teams create content that users can understand without effort.
- Keep articles short and clear: Short paragraphs, clear explanations, and scannable formatting make answers easier to digest, especially when users are in a hurry.
- Focus on one topic per article: When each article solves a single problem, readers avoid confusion and reach the right solution without sifting through unrelated details.
- Use visuals and screenshots: Visual cues reduce cognitive load, turning complex steps into something users can follow at a glance.
- Maintain consistency: A familiar structure across articles builds trust and helps readers predict where information will be, even when the topics differ.
- Add internal links: Contextual links keep users moving between related topics and encourage them to explore deeper without hitting a dead end.
How Different Teams Use a Knowledge Base
Across departments, a knowledge base becomes the central place teams rely on to work faster and reduce repetitive questions.
HR (Human Resources)
HR relies on knowledge bases to answer repetitive employee questions and simplify onboarding, especially in distributed or fast-growing teams. Clear, searchable guides reduce back-and-forth and improve employee self-service significantly.
Real-world example: Hotjar’s “Working at Hotjar” page maintains a transparent, employee-facing HR knowledge base that covers PTO, payroll, benefits, remote work guidelines, and cultural expectations. All of it is organized in a simple, easy-to-navigate handbook format.
Finance
Finance teams use knowledge bases to manage compliance documents, audit trails, and regulatory updates across distributed teams. Strong KM systems help institutions control risk, track regulatory changes, and maintain consistent information.
Real-world example: PwC’s internal knowledge hub is a model for financial institutions that need consistent, up-to-date guidance on compliance, audit requirements, and regulatory changes.

Operations
Operations teams depend on knowledge bases to document SOPs, reduce training time, and protect institutional knowledge during turnover. Teams with high complexity or frontline workforces see major efficiency gains from standardized processes.
Real-world example: Shopify documents detailed internal SOPs and process playbooks that help new employees onboard quickly and maintain operational continuity.

Customer Service
Customer service knowledge bases help teams deflect repetitive tickets and speed up resolutions. Self-service content gives customers a quick path to answers, allowing agents to focus on more complex requests.
A Reddit team saw 90% of users find answers directly in their Help Center, reducing the need for agent involvement entirely.
Real-world example: Hiver, a customer service platform, uses its own knowledge base to deflect common queries across email, live chat, and WhatsApp. Teams using Hiver report faster resolutions because agents can search, reference, and share articles without leaving their inbox workspace.

Engineering/Technical Teams
Technical teams use knowledge bases to store build guides, architectural decisions, runbooks, and troubleshooting steps.
For example, Instagram Engineering publicly shares technical documentation and internal learnings, showing how structured knowledge accelerates problem-solving.

ITSM (IT Service Management)
IT teams use knowledge bases to standardize troubleshooting and reduce escalations, especially for recurring issues like password resets or access problems. Many IT orgs report measurable gains once routine fixes are documented and searchable.
What to Look for in a Knowledge Base Platform
Different teams depend on a knowledge base for different reasons, so choosing the right platform starts with understanding what each function needs.
- Customer support teams care about ticket deflection, AI-powered search, and fast retrieval.
- HR teams focus on clean internal documentation, policy management, and employee self-service.
- ITSM teams need structured workflows, version control, and knowledge capture tied to ticket lifecycles.
- Finance and Operations teams typically look for compliance tracking, approval trails, and consistent SOP documentation.
A platform should adapt to these goals, not force teams into rigid structures.
Key Criteria to Evaluate
- Powerful Search: AI-driven search that understands intent, misspellings, and natural language.
- Flexible Structure: Categories, templates, and tagging that match how your teams organize information.
- Collaboration Tools: Draft workflows, commenting, approvals, and clear ownership for updates.
- Multichannel Access: Knowledge surfaced across email, chat, portals, mobile, and AI assistants.
- Version Control: Track changes, roll back updates, and maintain compliance where required.
- Analytics: Insights into what users search for, where they get stuck, and which articles drive deflection.
- Security & Permissions: Role-based access for HR, finance, and IT documentation.
- Automation: Suggested articles, automated routing, and knowledge recommendations based on context.
Popular knowledge base software solves different problems. For example, Zendesk Guide works well for customer help centers. Notion is excellent for flexible team wikis. Hiver takes a different approach by bringing the knowledge base directly into your support workspace.
If you want a tool that keeps self-service and customer conversations in one place, Hiver is a strong fit.
Hiver is an AI customer service platform, bringing email, chat, WhatsApp, voice, and self-service into one workspace. Its built-in knowledge base gives teams an easy way to create articles, organize content with categories and tags, and publish updates without any technical setup.
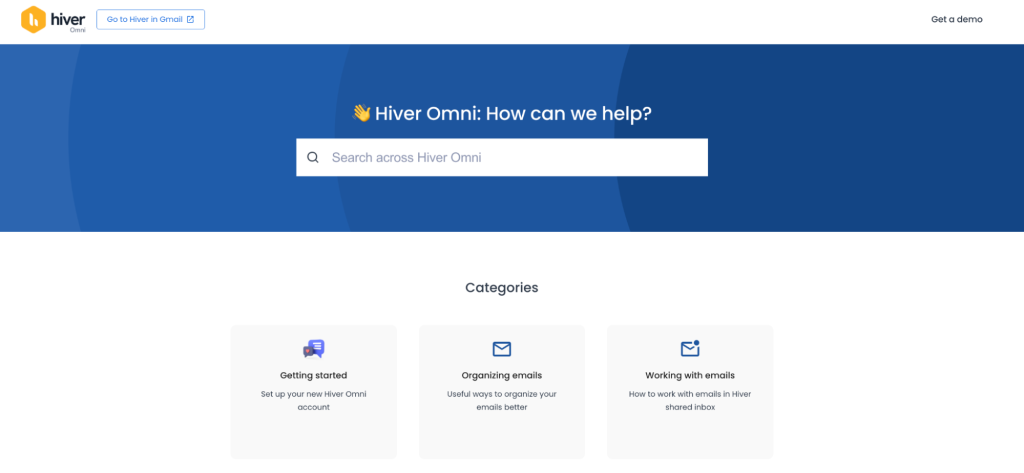
AI strengthens the experience by improving search accuracy, suggesting the right articles automatically, and powering self-service across chat, email, and WhatsApp.
The shift toward AI-enabled knowledge tools reflects broader workplace trends. Microsoft’s 2023 Work Trend Index shows that 70% of employees are ready to delegate as much work as possible to AI to reduce their load, making intelligent knowledge systems even more valuable.
Hiver’s combination of simple structure, quick setup, and AI assistance makes it a practical fit for support, HR, and IT teams.
Many teams choose it for the clarity and speed it provides without the overhead of managing a complex tool.
The Future of Knowledge Bases
The global knowledge management market is expected to grow from about $13–14 billion in 2026 to over $30 billion by 2030, and AI is a major driver of that shift. AI is reshaping how knowledge bases work by making it faster to create, organize, and retrieve information.
Nearly 75% of people say they’re comfortable using AI for analytical or creative tasks, and 78% of service leaders report that customers prefer to solve issues on their own.
These trends show why knowledge bases will remain essential for modern customer service and team collaboration.
As customers increasingly prefer self-service, organizations are moving toward integrated, AI-enabled knowledge systems that work across email, chat, and messaging tools.
Platforms like Hiver already support this shift by combining a unified knowledge base with email, live chat, and WhatsApp, so answers are always available wherever conversations happen.If you want a knowledge base that works efficiently across email, chat, and WhatsApp, Hiver’s knowledge base gives you an easy, integrated way to support customers with smarter self-service.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is a knowledge base vs a help center?
A knowledge base is the full repository of articles, guides, and documentation created by your team. A help center is the user-facing site where customers or employees access the knowledge base content.
2. What is knowledge base software?
Knowledge base software helps teams create, store, organize, and publish information in a searchable format. It centralizes documentation so users can quickly find answers without back-and-forth.
3. What is a customer service knowledge base?
A customer service knowledge base is a library of FAQs, troubleshooting steps, and how-to guides that help customers resolve issues on their own. It reduces ticket volume and improves support efficiency.
4. What is the value of a knowledge base?
A knowledge base improves self-service, reduces repetitive questions, and gives teams a single source of truth. It also boosts resolution speed and minimizes dependency on individual experts.
5. What type of data is provided in a knowledge base?
Knowledge bases typically include FAQs, step-by-step instructions, troubleshooting flows, policy documents, onboarding material, and product or process documentation.
6. What is a knowledge base article?
A knowledge base article is a standalone guide that explains one task, question, or issue in detail. It usually includes steps, visuals, tips, and links to related content.
 Skip to content
Skip to content