The most important thing you can do while creating a customer success journey map is to put yourself in the customer’s shoes. I know that sounds obvious, but many companies tend to unintentionally skip that part.
This is something that customer success leader Rachel Provan also points out. She highlights that most “journey maps” are really just SOPs in disguise. They focus entirely on what the company wants, not what the customer has to do to get results.
That’s why, in this article, I’ll show you how to create a customer success journey that maps out every step you and the customer must take to achieve their goal with your product or service.
TL;DR
A Customer Success Journey is a clear plan that shows each stage a customer goes through, from learning about a product to using it, renewing it, and recommending it. The goal is to help customers get value fast, find problems early, and help teams work together to improve retention.
– Who it helps: Customer success, support, onboarding, product, sales, and ops teams.
– Why it matters: It reduces onboarding drop-offs, finds churn risk early, and makes renewals smoother.
– What it includes: The stages, customer goals, key touchpoints, owners, milestones, and success metrics.
– Where it falls short: When it’s outdated, has no clear owner, or teams don’t use it daily.
Table of Contents
- What is a Customer Success Journey?
- What Are the Key Stages of a Customer Success Journey?
- What are the Benefits of Mapping Your Customer Success Journey?
- What Are the Key Elements to Map in a Customer Success Journey?
- 9 Steps to Create ther Best Customer Success Journey
- 1. Define Customer Success Goals and Vision
- 2. Facilitate Team Collaboration
- 3. Create Detailed Customer Personas
- 4. Map Out All Stages of the Customer Journey
- 5. Identify and Align Departmental Roles at Each Stage
- 6. Set and Monitor Customer Milestones
- 7. Use Customer Data to Find High-Impact Opportunities
- 8. Turn the Sales Journey into a Strong Start for Customer Success
- 9. Track Customer Success Metrics
- Turn the Customer Success Journey Mapping into a Repeatable System
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is a Customer Success Journey?
A customer success journey is the complete experience a customer has with a company. It starts when they first hear about a product or service and continues to the post-purchase interactions and beyond.
It is not a single straight path. It includes how someone finds your brand, learns about your product, decides to buy, gets set up, and starts seeing value. Over time, some customers may also share their experience with others.
A customer success journey works best when both sides grow together. The customer reaches the goals they wanted when they bought the product. The business benefits when customers keep getting value. When customers succeed, the company succeeds too.
Recommended reading
What Are the Key Stages of a Customer Success Journey?
A customer success journey has six stages: Awareness, Consideration, Decision & Purchase, Onboarding & Adoption, Usage & Retention, and Advocacy. Mapping these stages helps you understand what customers need at each point and what your team should do next, so customers achieve outcomes sooner and continue using your product over time.
Here’s what you need to know:
| Stage | What the customer wants | What your team should do |
|---|---|---|
| Awareness | Understand the problem and see what’s possible | Educate, build trust, and make the value clear |
| Consideration | Compare options and reduce risk | Share proof, answer questions, and remove friction |
| Decision & Purchase | Feel confident choosing you | Make buying simple and set expectations early |
| Onboarding & Adoption | Get set up and see value quickly | Guide setup, explain the “first win,” and support early use |
| Usage & Retention | Keep getting value without effort | Spot drop-offs, offer help at the right time, and stay consistent |
| Advocacy | Share success and feel recognised | Ask for reviews/referrals at the right moment and reward loyalty |
Let’s take a look at each stage in a bit more detail:
Stage 1: Awareness
A potential customer realizes they have a problem and discovers your brand as a possible solution. They’re curious but skeptical. They’re exploring options and may not even know your product exists yet.
Key touchpoints:
- Blog posts or educational content that addresses their problem
- Social media discovery or word-of-mouth recommendations
- Paid ads targeting their pain point
- Industry events or webinars
- Search results when they look for their problem
✅ What you can do: Educate. Show them you understand their problem and that solutions exist. Build awareness without being pushy.
💡Pro Tip: If people read your content but never ask for a demo or trial, either the problem isn’t strong enough, or your message isn’t clear.
Stage 2: Consideration
They’ve identified a need and are now actively researching solutions. They’re comparing your product against competitors. They want to know: “Is this the best option for us? What’s the cost? Will it actually work for our use case?”
Key touchpoints:
- Product demos or trial access
- Comparison content (your product vs. competitors)
- Customer reviews and case studies
- Sales conversations
- Free trials or freemium versions
- Documentation or feature overviews
✅ What you can do: Reduce risk. Be honest about fit, share clear pricing and case studies, and answer tough questions so they can compare options confidently.
💡Pro Tip: If prospects keep going quiet after demos or trials, you’re probably not addressing their real risks. Review the questions they ask most and update your proof and messaging.
Stage 3: Decision and Purchase
The customer is ready to commit and is comparing final options, terms, and timing. Once the contract is signed, they’ve formally chosen you, but the deal is still fragile. They want clarity on what happens next, when they’ll see value, and who will own what on both sides.
Key touchpoints:
- Contract signing or payment processing
- Welcome email from your team
- First communication with their assigned account manager or CS rep
- A Setup call or a kickoff meeting
- Initial onboarding materials
✅ What you can do: Make buying simple and predictable. Keep pricing and terms clear, confirm who signs off, and agree on goals, timelines, and owners before the contract is finalized. Introduce the customer success or implementation lead early and share a one-page plan for the first 30–90 days.
💡 Pro Tip: Before you mark a deal “closed won,” confirm who owns onboarding on their side, what success looks like in the first 90 days, and how you’ll measure it.
Stage 4: Onboarding & Adoption
The critical post-sale phase is where customers set up your product, learn how to use it, and have their first “aha!” moments. Overwhelmed but hopeful. There’s a lot to learn. They want to see value quickly, but they may feel lost or confused.
Key touchpoints:
- Onboarding training sessions (live or self-paced)
- Product walkthroughs or tutorials
- Help documentation and knowledge base articles
- In-app guidance and tooltips
- Check-in calls with your support or CS team
- Quick-win guides (how to achieve their first goal)
✅ What you can do: Guide them step by step. Break setup into clear tasks, offer help where people usually get stuck, and create a simple path to the first win.
💡Pro Tip: If customers don’t see real value in the first 30–60 days, they’re more likely to leave. Make sure onboarding leads them to one clear “first win” as early as possible.
Stage 5: Usage & Retention
Customers are now actively using your product, realizing ongoing value, and approaching renewal time. Engaged (or at risk), they’re either getting consistent value and becoming loyal, or they’re disappointed and considering alternatives.
Key touchpoints:
- Regular check-in meetings or business reviews
- Usage analytics and performance reports
- Educational webinars on advanced features
- Support tickets and help requests
- Renewal conversations
- Upsell or expansion opportunities
- Customer success surveys
✅ What you can do: Monitor, optimize, and expand. Track whether customers are achieving their goals. Provide proactive support. Look for opportunities to help them get more value (which naturally leads to upsells).
💡Pro Tip: If customers stop using key features or log in less often, don’t wait. Reach out early with a quick check-in, training, or a simple guide.
Stage 6: Advocacy
Happy, successful customers become loyal advocates. They renew contracts, expand their use, and refer others. Customer mindset: Satisfied and trusting. They see your product as essential to their success and are willing to recommend you.
Key touchpoints:
- Testimonials and case study requests
- Referral programs
- Customer advisory boards or user conferences
- Social proof and reviews
- Repeat purchases or expansions
- Word-of-mouth recommendations
✅ What you can do: Thank them for their loyalty. Create opportunities for them to share their success with others. Make referrals easy and rewarding.
💡Pro Tip: If happy customers still don’t want to give a quote or referral, ask why. Their answers will tell you what’s missing from your experience..
What are the Benefits of Mapping Your Customer Success Journey?
Mapping a customer success journey helps you identify where customers drop off, align teams on what ‘success’ looks like at each stage, and improve retention by fixing the moments that create friction.
Let’s look at the benefits in a bit more detail:
1. Develop a better understanding of your customers
A journey map lets you see things from the customer’s perspective, like how they think and feel at each stage, what obstacles they encounter, and what actually matters to them. This deeper understanding reveals gaps between what you think customers need and what they actually need, helping you build better onboarding, support, and product experiences.
2. Improve your customer retention rate
Did you know that acquiring new customers costs about 5x more than retaining existing ones? That’s why customer retention has such a big impact on your bottom line. A well-mapped customer success journey helps you spot the exact moments where customers are likely to drop off, like getting stuck during onboarding or struggling with a key feature. By identifying these friction points early, you can step in proactively and prevent churn.
3. Develop a customer-centric mindset in your company
A journey map breaks down silos between teams by forcing everyone to see the customer experience as one connected story, not isolated touchpoints. When Sales, Support, Product, and Marketing all reference the same map, they stop optimizing for department goals and start rallying around what actually matters: the customer’s success.
Recommended reading
How to Build a Culture of Customer Centricity in Your Organization
What Are the Key Elements to Map in a Customer Success Journey?
A customer success journey map should capture what happens at each stage and what customers need to keep moving. At minimum, you should map four things: touchpoints (where they interact with you), milestones (what progress looks like), emotions (what they’re feeling), and pain points (what slows them down). Let’s discuss them below:
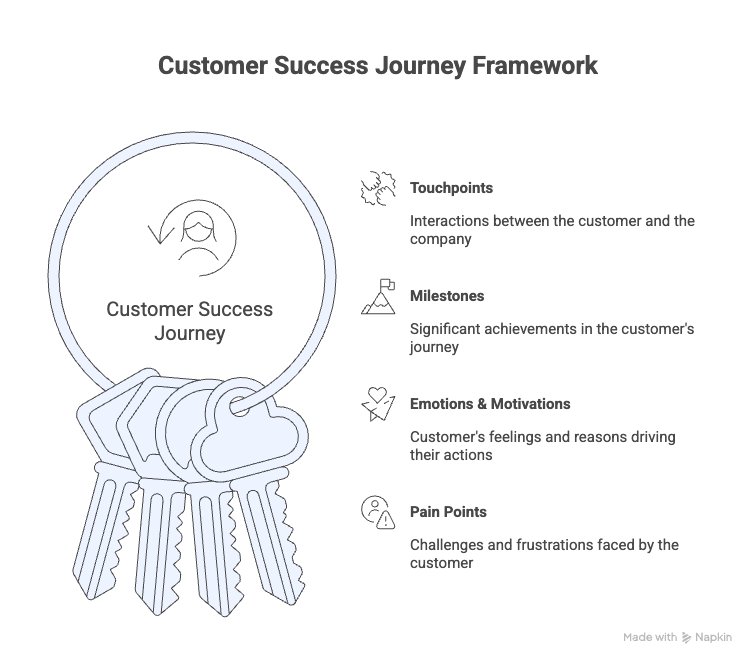
1. Touchpoints
Touchpoints are every moment a customer interacts with your company. These can include:
- Discovering your website or landing page
- Reading your emails or social media posts
- Attending a webinar or demo
- Speaking with a sales rep
- Logging into your product for the first time
- Reaching out to support
- Attending a Quarterly Business Review (QBR)
- Seeing an in-app notification or help article
Note: Each touchpoint is an opportunity to either reinforce their decision to choose you or create friction. Mapping these helps you ensure no customer falls through the cracks.
2. Milestones
Milestones are the key wins. These are the moments when a customer takes a meaningful step forward. For example:
- First Login: The customer accesses the product for the first time
- Profile Setup: They complete their account configuration
- First Feature Use: They take their first real action in the product
- First Value Delivered: They see tangible results (e.g., their first report or saved time)
- 30-Day Mark: They’ve been using the product consistently
- Feature Adoption: They’ve mastered a key feature you want them to use
3. Emotions & Motivations
Every customer feels something at each stage. Understanding these emotions helps you meet them with the right message or support. For example:
- During Awareness: Curiosity mixed with skepticism. (“Does this really solve my problem?”)
- During Consideration: Comparison anxiety. (“Am I making the right choice?”)
- During Onboarding: Overwhelm or anxiety. (“This is complex. Will I figure it out?”)
- After First Value: Relief and excitement. (“Oh, this actually works!”)
- During Long-term Use: Confidence and routine. (“This is just how we work now.”)
- At Renewal: Either contentment or doubt, depending on their journey.
Note: Understanding these emotions allows you to tailor your communication effectively. For example, at the time of onboarding, instead of sending just the checklist, you can also reassure them by saying: “Hey, here’s a quick 5-minute setup. You’ve got this.”
4. Pain Points
Pain points are the friction, confusion, or obstacles customers encounter. Common examples include:
- Complex or non-intuitive navigation in your product
- Lack of training materials or unclear documentation
- Long onboarding timelines that delay time-to-value
- Integration issues with the tools they already use
- Unclear ROI or how to measure success with your product
- Poor communication or unclear next steps after purchase
- Limited or slow support when they need help
9 Steps to Create ther Best Customer Success Journey
Whether you’re building a customer success journey from scratch or improving an existing one, these nine steps will help:
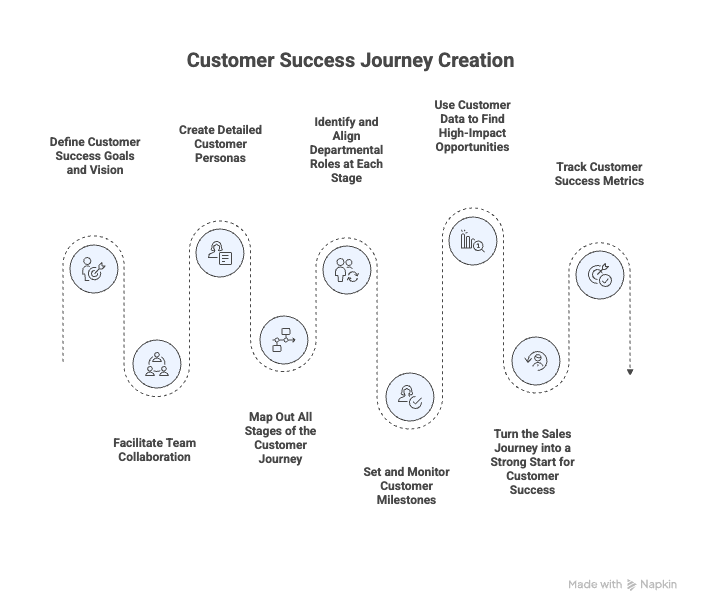
1. Define Customer Success Goals and Vision
Good customer success comes down to three things: building trust, understanding what customers need, and helping them see results again and again. So, start by getting clear on what you want customers to achieve and what your business needs from the relationship. When you get this right, you’ll usually see higher satisfaction, better retention, and more long-term revenue.
Here are some things to keep in mind while framing your customer success goals:
- Simplify Goals and Break Them Down into Sub-Goals: Overloading your team with too many targets can lead to confusion and a lack of focus. It’s better to aim for fewer impactful goals. You can also divide larger goals into smaller, manageable sub-goals. This approach provides a sense of achievement and keeps the team motivated. For example, the goal of improving the NPS score could involve sub-goals like conducting customer interviews or enhancing online support resources.
- Assign Responsibility: Designate an owner for each goal and sub-goal to ensure accountability and avoid duplicating efforts. This helps in streamlining tasks and maintaining a focused approach.
For instance, in a marketing team, you can assign one team member to oversee the goal of increasing website traffic, while another is responsible for the sub-goal of enhancing social media engagement, ensuring both areas are efficiently managed without overlap.
- Link Goals to Daily Work: Ensure that daily tasks are clearly connected to the broader goals. For example, every support ticket resolved by the customer service team should be linked to the larger goal of improving customer satisfaction and product usability.
2. Facilitate Team Collaboration
When teams collaborate effectively, customers notice. They get consistent answers, and their issues get resolved faster.
Here are some tips to boost team collaboration:
- Align on shared goals. Don’t just give each team its own targets. Make sure Sales, CS, Product, and Support all share a common goal: customer success. Everyone wins when the customer wins, and collaboration follows naturally.
- Use customer service platforms that let you collaborate easily. Prefer customer service tools that let teams communicate in real-time without endless email chains. Platforms like Hiver let you collaborate directly on customer conversations. You can add notes, @mention teammates, and share email drafts. This means no context gets lost in handoffs.
- Make sure everyone understands how they fit into the big picture: Try to make each team member understand the importance of their role to ensure they are motivated and contribute effectively.
For instance, in a retail team, customer service representatives should be shown how their prompt responses directly lead to higher customer satisfaction and repeat business, highlighting the importance of their individual roles.
- Choose leaders who bridge departments: Look for leaders who understand both the technical side and the human side. They should be able to translate between the Product’s roadmap and Support’s customer feedback, and help teams see how they depend on each other.
- Encourage Compromise: Teach the team to navigate differing opinions and find common solutions, maintaining smooth workflow and cooperation.
3. Create Detailed Customer Personas
Crafting customer personas involves developing in-depth profiles based on real customer behaviors, motivations, and preferences. What do they do for work? What problems keep them up at night? What does success look like to them?
The goal is to see your customers as real people with real needs, not just names in a spreadsheet. When you do this, you can tailor your approach to what actually matters to them.
Here are some best practices to execute this:
- Conduct Interviews: Direct conversations with customers provide invaluable insights. Target a representative sample across different segments to identify trends and commonalities.
- Use Web Analytics: Web analytics offer quantitative data on customer behavior. This can help you understand their interaction with your products or services better. You can track page views, clicks, and scroll depth to see how users navigate your site and identify popular entry points, common paths, and potential drop-off points. Tools like Google Analytics, Adobe Analytics, and Mixpanel can help you do this.
- Analyze and Segment: Segment your audience into personas based on collected data, focusing on common behavioral attributes.
For example, let’s consider an e-commerce website. Data analysis can reveal three distinct customer personas: ‘Bargain Hunters’ who frequently visit sale pages, ‘Trend Followers’ who click on new arrivals, and ‘Loyal Customers’ who regularly purchase and engage with loyalty program emails.
- Validate your assumptions. Use real customer data to back up what you think you know about your customers. If you think a certain group of customers values fast support, check if they actually use your support channels more frequently.
Here is a sample customer persona for reference:
An example of a complete customer persona for an e-commerce website specializing in eco-friendly home goods:
Name: Emma
Demographics:
– Gender: Woman
– Age: 30
– Location: Seattle, WA
– Education: Bachelor’s Degree
– Job Title: Store Manager
– Income: $60,000-$80,000
– Family Life: Married, expecting her first child
Struggles your product/service could address:
-Needs: Eco-friendly, safe products for home and baby
-Motivations: To provide a healthy, environmentally-conscious lifestyle for her family
-Pain Points: Difficulty in finding affordable, eco-friendly products; time constraints for researching product ingredients
Persona’s Journey
Emma actively seeks eco-friendly products for her home and baby. She values transparency in product sourcing and appreciates educational content. Effective engagement with Emma involves clear product labeling and targeted content marketing.
This streamlined version of Emma’s journey focuses on her key activities and preferences, directly relating to how your eco-friendly home goods e-commerce website can effectively engage with her.
4. Map Out All Stages of the Customer Journey
When you map out the customer journey, you understand how customers interact with your brand or product at every stage. You also get answers to questions like, ‘Are they having issues using key features?’ Is the user experience smooth, or is there room for improvement?
The bonus with finding these gaps is that when you fix them, it makes the user journey easier for your customer, thus leading to better engagement and satisfaction.
Here’s how to do it:
- List Key Stages: Determine the essential stages in the customer journey, such as awareness, consideration, purchase, and retention.
- Capture real touchpoints: For each stage, write down every way customers interact with you. This might include your website, emails, support tickets, onboarding calls, product usage, and renewal conversations.
- Mark friction points. This is the critical part. Use customer feedback, support tickets, and usage data to spot friction points. Where do customers drop off? Where do they ask for help repeatedly? Where do they get confused? These are your pain points.
- Understand what customers need at each transition. Customers don’t move smoothly from one stage to the next on their own. They need something from you. During onboarding, they need training. During retention, they need to see ROI. Make these needs explicit in your map.
- Use real customer data, not assumptions. Collect feedback through surveys, interviews, and support conversations. Tools like Hiver can help you gather customer feedback using CSAT surveys.

- Update your map regularly. As your product evolves, as your customer base changes, and as market conditions shift, update your map. Review it quarterly with your team and adjust based on what you’re learning.
5. Identify and Align Departmental Roles at Each Stage
When you map the customer success journey, also map who owns what. For each stage, note which team is responsible, who supports them, and when they need to hand over to the next team. Think of it like a relay race: each runner knows when to pass the baton, so the customer never gets dropped.
This is more than just making a list of tasks. When marketing, sales, customer success, support, and product all see their role on one shared map, it’s much easier for them to coordinate and spot gaps in the experience.
Here are some tips to do that:
- Define Responsibilities: Clearly outline the responsibilities of each department at every stage of the customer journey. Ensure that these roles are well understood and accepted by all team members.
For instance, in a tech company, R&D develops the product, marketing strategizes the launch, and sales handles the market introduction, with each department aware of its specific deadlines and tasks.
- Facilitate Interdepartmental Communication: Encourage frequent communication between departments. This can be achieved through regular meetings, shared platforms, or collaborative projects. For example, customer support can share their observations on what features customers are requesting every month with the product team.
- Align Goals Across Departments: Don’t stop at “who does what.” Add what each team is trying to achieve at that stage (e.g., “Onboarding: help the customer reach their first value moment in 30 days”). This keeps everyone pointed at the same result.
- Monitor and Optimize Collaboration: Regularly assess how well departments are collaborating and make adjustments as necessary. This could involve redefining roles, introducing new collaboration tools, or providing additional training.
6. Set and Monitor Customer Milestones
Customer milestones should reflect what customers are trying to achieve, not just what your business wants from them. They mark meaningful moments such as “first login,” “first workflow set up,” “first report generated,” or “first renewal.” When you track these consistently, you can quickly see who is on track, who needs help, and where your journey might be broken.
Here’s how to make milestones work:
- Link Milestones to Customer Goals: Start from the outcomes your customers care about (e.g., “reduce response time,” “increase revenue from X channel”) and work backwards. Each milestone should represent a concrete step toward those outcomes, not just an internal task completed.
- Communicate Milestones to Customers: Keep your customers informed about these milestones and what they mean for their journey and success. You can do this through email campaigns or add them to your monthly customer newsletter.
- Track and Analyze Milestone Achievement: Use your CRM, customer service platform, or product analytics to monitor who is hitting which milestones, how long it takes, and where drop-offs occur. Patterns here will tell you where to improve onboarding, training, or product UX.
- Adjust Milestones as Needed: Be flexible and willing to adjust milestones based on customer feedback, changes in customer behavior, or new insights about the market.
7. Use Customer Data to Find High-Impact Opportunities
This step is about using customer data to spot patterns, preferences, and pain points, so you can focus on changes that will make the biggest difference.
Let’s take the example of an online clothing store. They notice that returns are going up. When they look at order history and customer feedback, they find the main issue is sizing. So they create a clearer sizing guide. After that, returns drop, customers are happier, and more people buy again.
By looking at customer interactions, feedback, and behavior, you can see what’s not working, fix it, and better match what customers need. Here’s how you can do that:
- Look for friction points. Look for themes that keep showing up in tickets, onboarding calls, or feedback. If customers ask the same question again and again, something is unclear (product, docs, or messaging).
- Track where customers stall. Identify the step where progress slows down, like “connected integration,” “invited teammates,” or “completed first workflow.”
- Identify “Power User” behaviors. What do your most successful customers do that others don’t? Do they use a specific integration? Do they log in daily? Once you identify these “success behaviors,” you can nudge other customers to do the same.
- Watch for early risk signals. As Kel Kurekgi, Director of Developer Support at Zapier, puts it: “Most customers won’t tell you when they’re unhappy. They’ll just leave. By the time you notice they’re gone, it’s too late.” It becomes important to proactively look for non-verbal cues from your customers.
AI sentiment analysis can help with this to some extent by detecting dissatisfaction in customer conversations. Platforms like Hiver use AI sentiment analysis to flag these shifts automatically. It can analyze the emotional tone of customer conversations over time and tell you whether the sentiment is negative or positive.

- Spot upsell triggers. Data can also tell you when a customer is ready for more. If a customer consistently hits their usage limits or adds new users, they’re likely ready for an upgrade conversation. This is a high-impact opportunity to increase revenue while delivering more value.
- Test small changes. Don’t overhaul everything at once. If you think improving your welcome email will increase login rates, test it. If you think a new help article will reduce tickets, try it. Small, data-backed experiments often lead to the biggest wins.
Recommended reading
8. Turn the Sales Journey into a Strong Start for Customer Success
The sales journey is often the first and most crucial part of the customer experience. By documenting key sales moments, standardizing what gets promised, and defining a clean handoff into onboarding, you set Customer Success up to deliver value faster and more consistently.
Here are a few tips to make that happen:
- Map Sales Touchpoints: List the moments customers interact with your team (demo, trial, pricing, security review, contract).
- Capture questions and concerns: Note what customers typically ask at each touchpoint and what proof they need to move forward (case studies, ROI, security docs).
- Set clear expectations: Document what Sales should and shouldn’t promise (timelines, onboarding effort, key limitations) to avoid mismatched expectations later.
- Define the handoff to onboarding: Specify what Sales must pass to CS (goals, stakeholders, use case, timelines, risks) and when the handoff happens.
- Track early signals: Use CRM and support/product data to identify risks early (stalled trials, unclear success criteria, missing stakeholders) and address them before onboarding begins.
9. Track Customer Success Metrics
Customer success metrics tell you if customers are getting value or drifting toward churn. Tracking them helps you spot problems early (like slow onboarding or low adoption) and decide what to fix next. Here’s how to approach it:
- Focus Key Metrics: Track metrics based on the stage you’re working on. For example, during onboarding, focus on time-to-first-value and early adoption. For ongoing support, track CSAT and CES. For long-term health, track NPS and renewal risk signals. You can easily track and analyze CSAT scores using built-in reports and dashboards in your customer service tool. Hiver can also help you track that.
- Identify patterns: Look out for trends such as features that generate the most tickets, customer drop-off points, or behaviors common among your most successful customers. To do this effectively, you need to capture the right data upfront. Reports and analytics in customer service tools like Hiver can also help you filter this data by generating custom reports with specific fields.

- Turn insights into clear actions. Once you’ve identified a pattern, translate it into a specific change. For example, improve onboarding for a confusing feature, adjust messaging for a certain segment, or add help content where people usually get stuck.
Recommended reading
Turn the Customer Success Journey Mapping into a Repeatable System
A strong customer success journey is more than a map. It’s a repeatable way to help customers reach value faster and stay longer. Use the steps in this guide to map the key stages, spot friction points, and make ownership clear across teams.
Start small. Pick one stage to improve first, usually onboarding or renewal. Fix the biggest bottleneck, measure what changed, and then move to the next stage. Once you’ve improved one stage, document what worked, roll it out across the journey, and review it quarterly so the system keeps working as you grow.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is a customer lifecycle?
A customer lifecycle is the full relationship a customer has with your business, from first discovery to renewal and beyond. It helps you understand what customers need at each stage, so you can reduce drop-offs and improve retention.
2. What are the 5 A’s of the customer journey?
The 5 A’s of the customer journey are: Aware, Appeal, Ask, Act, and Advocate. They explain how people move from discovering a brand to buying, and then recommending it to others.
3. What are the 5 E’s of the customer journey?
The 5 E’s of the customer journey are: Entice, Enter, Engage, Exit, and Extend. This framework is used to map and improve experiences from the first interaction through repeat usage and long-term loyalty.
 Skip to content
Skip to content












