User:“My order hasn’t arrived yet.”
Chatbot:“Your order was delayed and is now expected tomorrow. Would you like the tracking link or help with a refund?”
Interactions like this are becoming common. People now expect software to understand questions, follow the context, and respond in natural language, rather than forcing them through menus or forms.
The shift comes from conversational AI, systems designed to handle conversations rather than respond to single commands.
In this article, we explain what conversational AI is, how it works, how it differs from traditional chatbots and generative AI, and where it is used today.
Table of Contents
- What is Conversational AI?
- How Conversational AI Differs from Traditional Chatbots
- What Is the Difference Between Conversational AI and Generative AI?
- Key Components of Conversational AI
- Types of Conversational AI
- Benefits of Conversational AI
- Key Applications of Conversational AI
- How Conversational AI Works
- Common Challenges and Limitations of Conversational AI
- How to Implement a Conversational AI Strategy
- Future Trends in Conversational AI
- Conversational AI and the Future of Customer Interactions
- Frequently Asked Questions
What is Conversational AI?
Conversational AI is a type of artificial intelligence that lets computers communicate with people using natural, human-like language through text or voice.
Instead of relying on rigid scripts or predefined replies (like traditional chatbots), conversational AI systems understand user input, interpret intent, and provide relevant responses in real-time.
These systems can hold conversations over multiple turns. They remember context from earlier messages, and their responses also improve over time as they learn from more data.
How Conversational AI Differs from Traditional Chatbots
Traditional chatbots rely on predefined rules and keyword matching. They follow scripted paths and respond only when a user’s input closely matches what they expect.
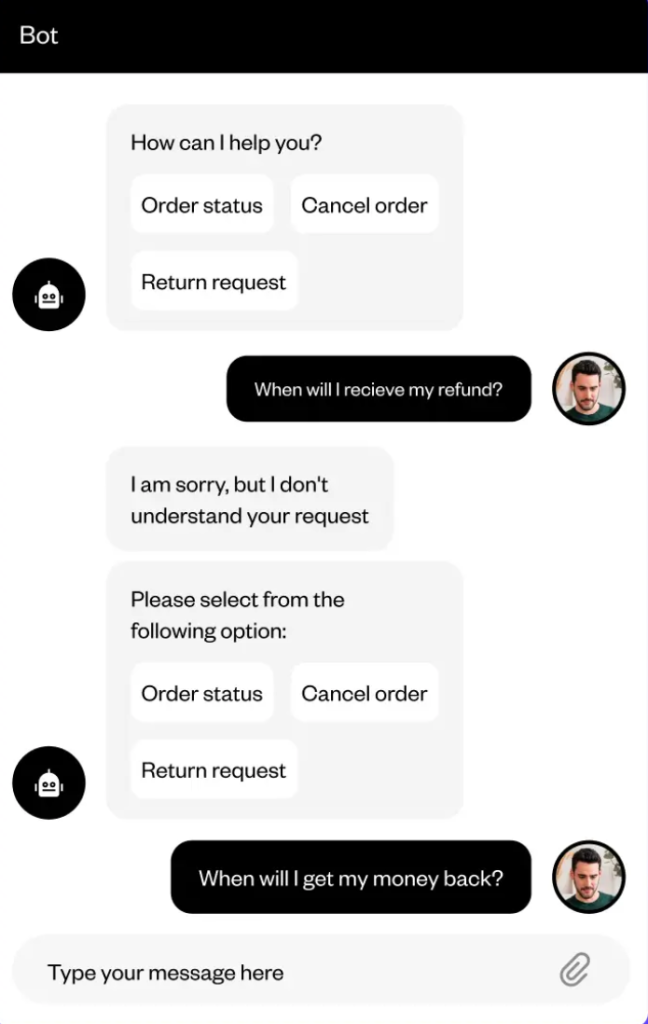
If the question is phrased differently or followed up, the chatbot often resets or fails to respond accurately.
Conversational AI works differently. It understands intent, keeps context, and adapts responses as the conversation continues.
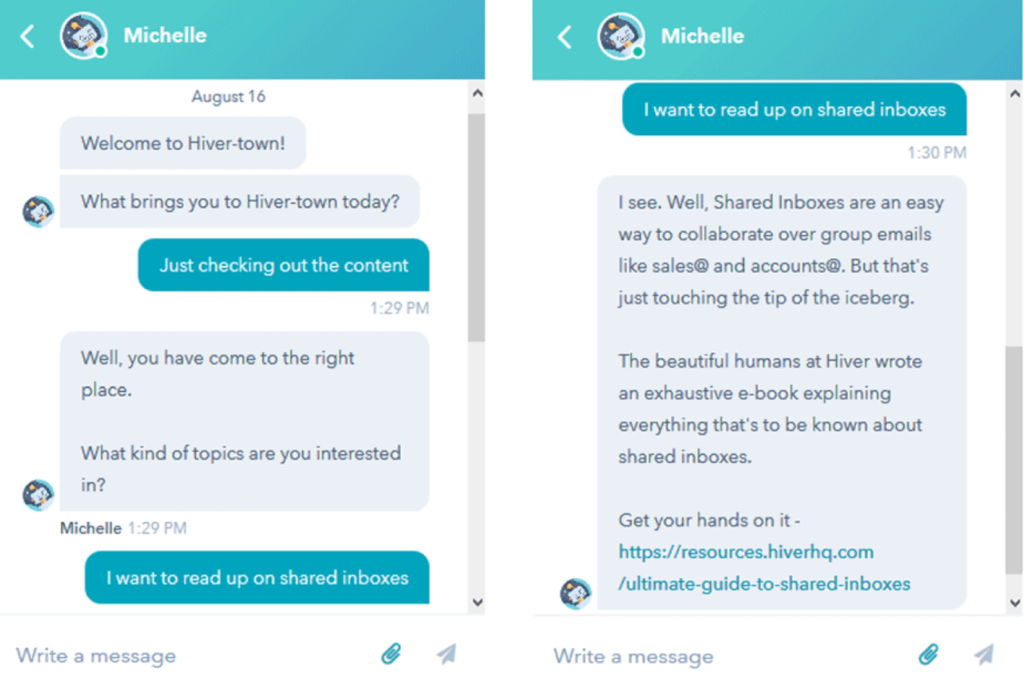
Instead of treating each message as a separate request, conversational AI connects messages into a single conversation. It can handle follow-up questions, clarify intent, and decide when to involve a human.
Traditional chatbots respond to commands. Conversational AI is built to hold conversations.
What Is the Difference Between Conversational AI and Generative AI?
The terms conversational AI and generative AI are often used interchangeably, particularly since tools like ChatGPT have become mainstream. They are related, but they are not the same.
Generative AI refers to AI systems designed to create new content based on a prompt. These systems generate text, images, code, or summaries by predicting what comes next, rather than managing a structured interaction or task.
Generative AI focuses on producing content based on a prompt, without requiring an understanding of the broader context of an interaction.
Conversational AI, on the other hand, is designed to guide a conversation. It tracks intent and context across multiple turns so each response builds on what came before.
| Aspect | Conversational AI | Generative AI |
|---|---|---|
| Primary purpose | Manage and complete conversations | Generate new content from prompts |
| Focus | Intent, context, and task completion | Creativity and content generation |
| Typical use cases | Customer support, virtual assistants, guided workflows | Writing, summarization, coding, image generation |
| Context handling | Maintains conversation history and user state | Context depends on prompt and session setup |
| Response control | Uses rules, logic, and guardrails | Responses are open-ended by design |
| Example | “Your order will arrive tomorrow. Would you like the tracking link?” | “Write an apology for a delayed order.” |
Key Components of Conversational AI
Conversational AI systems rely on several core components working together to understand users and respond appropriately. Each component plays a specific role in turning human language into meaningful, actionable responses.
1. Natural Language Processing (NLP)
NLP enables the system to process human language in text form. It helps break sentences into words, understand grammar, and recognize meaning, even when people phrase words in different ways.
NLP allows conversational AI to handle natural, informal language instead of requiring exact commands.
2. Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR)
ASR converts spoken language into text. This component is essential for voice-based conversational AI, such as voice assistants and call center automation.
It allows the system to interpret accents, pronunciation differences, and spoken input in real time.
3. Natural Language Understanding (NLU)
NLU focuses on intent and context. It determines what the user wants to do, not just what words they used.
NLU helps conversational AI understand whether a user is asking a question, making a request, or seeking clarification.
4. Machine Learning and Deep Learning
Machine learning enables conversational AI to improve over time. By learning from past interactions, the system becomes better at recognizing intents, handling edge cases, and responding accurately as conversations grow more complex.
Types of Conversational AI
Each type of conversational AI serves a distinct role in modern digital experiences. Here are the top three types:
1. AI Chatbots
AI chatbots interact through text-based conversations on websites, apps, and messaging platforms. They handle tasks like answering questions, resolving issues, and guiding users through workflows while maintaining context across messages.
2. Voice Assistants
Voice assistants enable users to interact using spoken language. Common in smart devices, call centers, and in-car systems, they rely on speech recognition and conversational AI to understand commands and respond naturally.
3. AI Copilots
AI copilots work alongside users within applications. Instead of replacing human actions, they assist with tasks by offering suggestions, summarizing information, and helping users complete work more efficiently during ongoing activities.
Benefits of Conversational AI
Here are some of the key benefits conversational AI brings to modern digital interactions:
- Faster responses: Conversational AI delivers instant answers and reduces wait times for users.
- Always available: Support stays accessible 24/7 without relying on agent availability.
- Natural interactions: Users ask questions in plain language instead of navigating menus or forms.
- Context-aware conversations: Follow-up questions stay relevant because earlier messages are remembered.
- Scales easily: High conversation volumes are handled without adding headcount.
- Consistent answers: Responses stay aligned with policies and shared knowledge.
- Improved efficiency: Repetitive questions are handled automatically, freeing teams to focus on complex work.
- Better handoffs: Conversations move smoothly to humans with full context preserved.
Key Applications of Conversational AI
Conversational AI is used wherever people interact with systems through questions or commands. Below are some of the most common applications today:
Virtual Assistants
Voice-based virtual assistants are now common at work and at home. Industry estimates project that there will be 8.4 billion digital voice assistants worldwide by 2028. These voice assistants reduce response times and lower support costs
Even financial institutions, such as Bank of America, use virtual assistants to assist customers in checking balances and reviewing transactions.
Generative AI–Powered Conversations
Generative AI is now built into many conversational interfaces to help systems respond more flexibly and naturally. In 2024, 65% of companies reported using generative AI regularly. Businesses use it to generate replies in real time, explain products, summarize information, and handle open-ended customer questions during conversations.
The payoff is tangible; 67% of AI-leading businesses saw revenue boosts of over 25% after adopting AI solutions, underscoring its value. These gains reflect how generative AI strengthens conversational experiences by improving response quality, speed, and scalability.
Customer Service
Conversational AI is used in customer service to handle high volumes of routine queries and reduce response times. Teams use AI-powered chat and email assistants to answer common questions, route conversations, and support agents during peak periods.
Ecommerce companies such as Golftini have used conversational AI–driven workflows to reduce manual triage by up to 80%. First-response times improved by around 60% without increasing support headcount.
Developer Tools
Conversational AI is also used in developer workflows. Gartner predicts that 30% of enterprises will use AI-augmented development and testing by 2025, up from 5% in 2021. Another survey indicates that 82% of developers use AI coding tools on a weekly basis, with reported time savings of 30–50% in coding and testing.
Smart Homes and IoT
Conversational AI acts as the interface for connected devices. There are over 400 million smart homes globally, where voice assistants control lighting, temperature, and appliances. Voice-based commerce is also growing, with projections estimating that $164 billion in voice-driven shopping will occur by 2025.
How Conversational AI Works
Conversational AI follows a series of steps that turn human input into meaningful responses. Each step plays a role in keeping conversations accurate, contextual, and natural.
Step 1: Processing The User’s Language (NLP)
User messages are analyzed to identify sentence structure, key terms, and language patterns. Natural language processing allows the system to handle different ways of phrasing the same request without relying on exact keywords.
Step 2: Converting Speech Into Text (ASR)
Voice interactions require spoken input to be converted into text before further processing. Automatic speech recognition enables conversational AI to work across voice channels while maintaining consistency with text-based conversations.
Step 3: Learning From Interactions (Machine Learning and Deep Learning)
Past conversations influence how the system responds over time. Learning models help improve intent recognition, adapt to new language patterns, and reduce errors without constant manual updates.
Step 4: Understanding Intent And Meaning (NLU)
User intent and relevant details are identified to determine the next action. Natural language understanding guides responses, triggers workflows, or escalates conversations to a human when needed.
Common Challenges and Limitations of Conversational AI
Here are some common challenges and limitations to be aware of when using conversational AI:
- Context loss: Conversations can break down when the system fails to remember earlier messages, leading to repetitive questions or incorrect responses.
- Training quality: Conversational AI depends heavily on the data it learns from. Poor, outdated, or incomplete training data reduces accuracy and reliability.
- Over-automation: Automating too much can frustrate users, especially when complex or sensitive issues require human judgment.
- Human handoff issues: Poorly designed escalation flows force users to repeat information or wait too long to reach a human, damaging the overall experience.
How to Implement a Conversational AI Strategy
Implementing conversational AI works best when the focus stays on user needs rather than technology alone. A structured approach helps avoid over-automation and poor experiences.
Step 1: Identify High-Impact Use Cases
Start with conversations that are frequent and predictable. Customer support questions, order tracking, appointment booking, and internal help requests often deliver the fastest value.
Step 2: Define Clear Conversation Goals
Each interaction should aim for a specific outcome, such as resolving an issue, collecting details, or guiding users to the next step. Clear goals keep conversations focused and useful.
Step 3: Prepare Training Data
Use real customer questions, FAQs, past chat transcripts, and help articles to train the system. Quality examples help conversational AI understand how users naturally phrase requests.
Step 4: Plan For Human Handoff
Some conversations require human judgment. Set clear rules for when and how conversations move from AI to a human to avoid frustration.
Step 5: Monitor And Improve Continuously
Review conversations regularly to spot missed intents, confusion, or drop-offs. Ongoing tuning helps improve accuracy as user behavior changes.
A step-by-step approach helps conversational AI deliver value without sacrificing the customer experience.
If you’re looking to apply conversational AI specifically to customer support, here’s a step-by-step guide on how to implement a conversational AI strategy for customer service the right way.
Future Trends in Conversational AI
Here are some of the key trends shaping how conversational AI is evolving in the coming years:
- More intentional human handoffs: Conversational AI is expected to get better at recognizing complex or uncertain situations. Instead of pushing for full automation, systems will escalate conversations more deliberately. Some reports already show handoffs increasing from 22% to 32% as AI learns when human involvement leads to better outcomes.
- Deeper personalization driven by real-time data: Conversational AI will increasingly combine customer history, real-time behavior, and generative AI. Responses are expected to adapt more dynamically to each user. Today, 66% of service leaders already use AI to personalize interactions, and that number is likely to grow.
- Multimodal conversations becoming standard: Text-only chat will not remain the default. Voice, images, and mixed inputs are expected to play a larger role, especially in support and banking. Early voice-based systems have already shown strong gains in customer satisfaction.
- Proactive and anticipatory interactions: Conversational AI is expected to move beyond reactive replies. Systems will offer help based on behavior and context, even before users ask. In some early cases, proactive voice assistants have driven customer satisfaction improvements of over 150% for specific interactions.
These trends point toward conversational AI that feels more natural, proactive, and tightly integrated into real-world workflows.
Conversational AI and the Future of Customer Interactions
Conversational AI is shaping how people interact with software, moving experiences away from rigid interfaces toward more natural, conversational exchanges.
It works best when it handles repetitive tasks reliably and supports humans rather than replacing them. Clear use cases, quality training data, and smooth handoffs keep conversations helpful and on track.
As expectations for instant, natural interactions continue to rise, conversational AI will play a central role in how businesses communicate, support users, and scale conversations across channels.
If you’re exploring how conversational AI fits into customer support workflows, platforms like Hiver make it easier to combine AI-driven conversations with human collaboration across email, live chat, and other channels.
You can start with a free trial to see how conversational AI works in a real support environment.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is the difference between chatbots and conversational AI?
Chatbots follow predefined rules and scripts, while conversational AI understands intent, maintains context, and handles multi-turn conversations more naturally.
2. How is conversational AI trained?
Conversational AI is trained using real conversations, FAQs, and examples that help it learn language patterns, intent, and how to respond accurately.
3. What problems does conversational AI solve best?
Conversational AI works best for handling repetitive questions, guiding users through processes, and providing quick, contextual responses at scale.
4. Can conversational AI work without human agents?
Conversational AI handles many requests on its own, but human agents remain essential for complex or sensitive conversations.
 Skip to content
Skip to content