Fast replies are great, but speed alone isn’t customer service management. A quick answer that misses the real problem creates repeat messages and frustrated customers.
Great support, as Simon Sinek says, comes from “understanding what the customer is trying to accomplish.”
Customer service management is the system that makes this possible. It keeps support organized, connected, and reliable, even when requests grow. It ensures every message has an owner, context travels with the customer across channels, and routine work doesn’t slow agents down.
In this blog, we’ll discuss:
- What customer service management means in 2026 and why it matters
- Benefits of customer service management
- How to create a customer service management strategy
- Examples of teams managing customer service in real life
Table of Contents
- What Is Customer Service Management?
- Why is Customer Service Management Important?
- What Are the Benefits of Customer Service Management?
- Tools Used for Better Customer Service Management
- 11 Steps to Build An Effective Customer Service Management Strategy
- 1. Build A Detailed Customer Profile
- 2. Set Clear Objectives
- 3. Choose the Right Customer Communication Channels (And Make Sure It’s an Omnichannel Experience)
- 4. Build A Skilled Team
- 5. Use the Right Customer Service Software
- 6. Define Metrics to Track Success
- 7. Personalize Customer Interactions
- 8. Leverage AI to Reduce Manual Work
- 9. Create Accountability Systems That Build Customer Trust
- 10. Streamline Feedback Collection and Action
- 11. Provide Self-service Options
- Customer Service Management Examples
- Build a Customer Service Management Strategy That Scales
- FAQs
What Is Customer Service Management?
Customer service management (CSM) refers to the systems, processes, and tools used to deliver customer support consistently and efficiently. It sets up a clear system to receive customer requests, assign them to the right person, track progress, escalate when needed, and solve issues without delays. This helps support staying reliable, even when requests grow.
CSM covers the end-to-end customer journey, from the first interaction with your brand, to purchase and onboarding, and then to post-sale support. The ultimate goal is to improve customer satisfaction, increase loyalty and retention, and boost critical business metrics such as revenue.
Why is Customer Service Management Important?
Customer service management is important because it helps teams stay organized and deliver good support, even as requests increase. When support teams don’t have a clear system, messages get lost, work slows down, and customers feel frustrated.
Here are the common challenges most companies struggle with:
- No clear owner: Marketing and sales promise one thing, but support is left to explain what’s actually possible. Product teams ship changes that confuse customers. Ultimately, nobody owns the entire experience from start to finish.
- Tracking the wrong metrics: Teams focus on tickets closed, handle time, or response speed. These can look good on reports, but they don’t always show the real customer experience. Customers can still feel unheard, stuck, or frustrated.
- Outdated playbooks: Teams rely on old scripts and processes that no longer match how customers use the product or how support actually works today.
Organizations that address these failures systematically unlock tangible benefits across the business. Let’s look at some of them below.
What Are the Benefits of Customer Service Management?
The benefits of customer service management include:
- Increase customer satisfaction: Customers get clearer answers with fewer follow-ups, which usually matters more than just a fast first reply.
- Customer loyalty and retention: Consistent, low-effort support builds trust and keeps customers from leaving when things go wrong.
- Reduce customer acquisition costs: When customers are happy, they tell their friends and family about it, which drives positive word-of-mouth marketing. A number of brands rely on this strategy rather than investing thousands of dollars in paid marketing. In fact, 91% of B2B buyers trust word-of-mouth recommendations.
- Improve efficiency: Clear ownership, routing, and workflows reduce handoffs and wasted time, so agents spend more time solving issues and less time managing work. In fact, the impact shows in the numbers, AI-powered workflows reduce average handle time by 56%.
- Improve agent productivity: Agents can handle more requests at the same time because they spend less effort searching for context, rewriting replies, and chasing internal updates.
- Lower support costs over time: Self-serve content and automation reduce repeat questions, so teams can handle more volume without hiring at the same pace.
- Improve team visibility and control: Reporting shows what’s driving volume, where SLAs slip, and which queues are overloaded, so you can staff and plan with real data.
- Enable proactive customer service: When you spot patterns early, you can fix problems before they create more tickets, escalations, or churn.
- Competitive differentiation: When your products are similar to those of competitors, support becomes a deciding factor. Customers remember the brand that made problems easier.
Recommended reading
Tools Used for Better Customer Service Management
Customer service management largely depends on the tools around it, like your CRM, knowledge base, automation, and reporting. When these tools work together, your team keeps customer context in one place and is able to provide consistent customer service. Here are the tools that make customer service management stronger:
1. Customer relationship management (CRM) software
CRM software keeps customer data organized. It stores contact details, past purchases, support messages, and customer preferences in one place. This helps agents respond with context instead of asking customers to repeat information.
Popular CRMs like Salesforce and HubSpot integrate with support tools to give teams complete context for every interaction.
2. Marketing automation tools
Marketing automation tools (like Mailchimp, Customer.io, and ActiveCampaign) help you stay in touch with customers through onboarding emails, follow-ups, and re-engagement campaigns. This kind of proactive communication can prevent avoidable support requests and keep customers informed about changes, new features, and resources.
3. AI customer service platforms
AI customer service platforms reduce manual work by tagging and routing requests, summarizing long threads, suggesting reply drafts, and pulling relevant answers from your help content. This helps teams resolve issues faster and stay consistent as volume grows.
They also support an omnichannel experience by keeping conversations from email, chat, voice, and other channels in one place, so context carries over when customers switch channels.
For example, tools like Hiver support an omnichannel setup and apply AI across the workflow, including tagging and routing, sentiment signals, summaries, reply drafts, and trend insights.
4. AI Chatbots and assistants
Most AI customer service platforms include AI chatbots and AI assistants that work alongside human agents. They handle common questions 24/7, like order status, account details, or basic troubleshooting.
5. Social media management tools
Customers often share feedback, ask questions, or raise complaints on Twitter, Facebook, LinkedIn, and Instagram. Social media tools monitor these mentions, route them to the right team members, and track response times so no customer message gets lost in the noise.
Recommended reading
11 Steps to Build An Effective Customer Service Management Strategy
Developing an effective customer service management strategy requires a thoughtful approach that aligns with your business goals and customer needs. Here’s a step-by-step guide for the same:
1. Build A Detailed Customer Profile
A strong customer service management strategy starts with understanding what your ideal customer profile (ICP) is and why they reach out. Define your main customer segments, the outcomes they care about, and the issues that come up most often. This helps your team respond with context and solve the real problem, not just the symptom.
Ask yourself these questions:
- Who gets the most value from our product, and what are they trying to achieve?
- What usually triggers them to contact support?
- What does a “good outcome” look like for them in a support interaction?
- What context changes the right response (plan tier, account type, region, contract terms)?
How to build it:
- Use support metrics (response time, resolution time, CSAT) to spot where the experience breaks.
- Review recent tickets and group them by theme (billing, bugs, onboarding, account changes).
- Look for repeat questions and common failure points (where customers get stuck).
- Use feedback and surveys to understand expectations and pain points.
2. Set Clear Objectives
Once you have a clear understanding of the customer, the next step is to decide what “better support” actually means for your team. Clear objectives help you prioritize the right work, align everyone, and avoid chasing vanity metrics.
Start with 2–4 goals. Keep them specific, measurable, and tied to outcomes customers can feel, not just numbers that look nice in a dashboard.
What good objectives look like:
- Reduce first response time for urgent tickets (e.g., from 2 hours to 30 minutes)
- Improve CSAT (e.g., from 3.9 to 4.3 out of 5)
- Reduce resolution time for priority issues (e.g., from 3 days to 1 day)
- Reduce repeat tickets for your top issues (e.g., cut repeats by 20% over a quarter)
How to set them
- Tie each goal to a customer pain point. If customers complain about delays, focus on response time. If they complain about bouncing between agents, focus on ownership and handoffs.
- Define what “good” looks like by priority. A billing escalation and a “how-to” question should not have the same target.
- Pick the metric, the target, and the timeframe. For example: “Improve CSAT from 3.9 to 4.3 by the end of Q2.”
3. Choose the Right Customer Communication Channels (And Make Sure It’s an Omnichannel Experience)
Customer service management works best when you support customers where they already are, without spreading your team too thin. Start with the channels that bring in the most requests and the most urgent issues. Then expand only when you can maintain the same level of service across every channel.
Just as important: treat these channels as one connected experience. Customers don’t think in “email vs chat.” They switch based on urgency and convenience. That’s why omnichannel support matters. If your channels don’t share context, customers have to repeat themselves, and agents waste time piecing the story together.
What to do:
- Identify where most requests come from today (email, chat, phone, social).
- Prioritize channels based on volume and urgency, not what seems trendy.
- Set clear expectations for each channel (hours, response targets, what belongs where).
- Make sure conversation history carries over when customers switch channels.
💡Pro Tip: Omnichannel only works when conversation history carries over across channels. If customers switch from chat to email and your team loses context, you’ll get repeat explanations, slower resolution, and more follow-ups.
Customer support tools like Hiver make it easy to set up an omnichannel workspace. You can manage email, chat, WhatsApp, voice (and more) in one shared workspace, so even when customers switch channels, the context stays in one place.

4. Build A Skilled Team
Support quality depends on hiring, training, and clear ownership. Even strong agents struggle when roles are unclear or when escalation paths are messy. So define expectations upfront, train for consistency, and keep coaching ongoing.
What to do:
- Define roles and ownership. Who handles new tickets? Who handles escalations? Who owns billing or technical issues? Make this clear from the start.
- Hire for judgment. Look for people who can write clearly, stay calm, ask good questions, and take ownership of a problem until it’s solved.
- Train for consistency. Your onboarding should cover product basics, tone guidelines, escalation rules, and how to handle tricky situations (refunds, outages, angry customers).
- Keep training ongoing. Run short refreshers after major product launches, policy changes, or when you see repeat issues climbing.
- Create a feedback loop. Review a small set of tickets each week as a team. Agree on what “good” looks like. Update playbooks and help content based on what you see.
Recommended reading
5. Use the Right Customer Service Software
If a “support tool” adds more tabs, more steps, and more admin work, it’s not a stack. It’s a slowdown. The right customer service tool helps centralize customer communication, route tickets to the right agents, drive faster internal collaboration on tickets, and also track team performance.
Here’s what to look for in a customer support tool:
- Ease of use: Look for an easy setup and an intuitive workspace.
- Clear ownership: You need ticket assignment, ownership, and escalation workflows so every request has a clear owner.
- Automation: Prioritize workflow automation, auto-tagging, priority rules, and auto-routing so routine work doesn’t pile up.
- Omnichannel support: Your tool should support omnichannel customer service with conversation history staying intact across email, chat, voice, and messaging.
- Self-service options: Look for tools with a knowledge base and a customer portal to deflect repetitive queries.
- Reporting: You need customer service analytics for response time, resolution time, SLA breaches, backlog trends, and workload distribution.
- Integrations: Prioritize CRM integrations, helpdesk integrations, and connectors to billing/order tools so agents don’t hunt for info.
- Security and controls: Look for role-based permissions, SSO, and audit logs so access stays clean and compliant.
- AI that removes busywork: Useful AI helps agents move faster and stay accurate, through summaries, suggested responses, tagging, routing, and even handling queries end-to-end.
💡Pro tip: Choose a customer support tool based on how your company runs support today, and what you expect to change over the next 12 months. If you need a system your team can adopt quickly with minimal training, and you want AI support for summaries, tagging, and routing, a tool like Hiver is a strong fit.
However, if your support operation needs advanced workflows, deeper customization, and strict admin controls, Zendesk is often better suited. If your priority is a simple, clean help desk experience with strong self-service and an agent-friendly interface, Help Scout is a good option.

6. Define Metrics to Track Success
Tracking the right metrics helps you see what is slowing your support team down and what customers are struggling with. It also helps you set clear targets, plan staffing, and catch issues early. But, instead of tracking everything, focus on a small set of metrics that fall into four buckets:
1) Customer experience metrics: These tell you how customers felt about the support. For example:
- Customer Satisfaction (CSAT): CSAT scores tell you how satisfied customers were after an interaction
- Customer Effort Score (CES): CES shows how easy it was for customers to get help
2) Speed and workload metrics: These show how quickly your team is responding and whether work is piling up. For instance:
- First Response Time (FRT): Measures how quickly the first response is provided after a customer submits a query. A shorter FRT indicates faster initial engagement.
- Average Resolution Time (ART): ART tracks the average time it takes to fully resolve customer issues.
- Backlog: How many open requests are waiting
- Ticket volume: How many requests does your team receive over a period
3) Quality and efficiency metrics: These help you spot repeat issues and process gaps.
- Escalation Rate: Measures how often tickets need to be escalated to higher-level support or management. Lower escalation rates indicate that most issues are resolved by frontline support.
- Repeat contact rate: How often customers come back for the same issue.
4) Business signal metrics (optional): These don’t measure support directly, but they show how support impacts the business.
- Customer Churn Rate: Tracks the rate at which customers stop using your product or service. A high customer churn rate may indicate dissatisfaction with support or overall experience.
- Net Promoter Score (NPS): NPS measures customer loyalty by asking, “On a scale of 0-10, how likely are you to recommend our company to a friend?” Based on responses, customers are classified as promoters, passives, or detractors.
Recommended reading
7. Personalize Customer Interactions
Did you know 52% of companies see increased customer loyalty through personalized service. But, personalization isn’t about using someone’s first name. It’s about showing you understand the customer’s situation and helping them reach the outcome they care about, with less back-and-forth.
Here’s what personalization looks like in practice:
- Use customer history to avoid repeat questions. Before you reply, check what the customer has already tried, what was promised last time, and what plan or account they’re on.
- Acknowledge the goal behind the request. Customers often describe the symptom, not the outcome. A better response is: “I see you’re trying to ship this today, so let’s fix this in the quickest, safest way.”
- Match tone to the situation. A billing dispute, an outage, and a how-to question should not get the same tone. Adjust based on urgency and emotion.
- Stay consistent across channels. If a customer starts on chat and follows up on email, your support should still feel like one continuous conversation.
- Keep handoffs clean when more people get involved. When a ticket needs a specialist, summarize what’s been checked and what the customer needs next, so the customer isn’t bounced around.
💡Pro Tip: Tools like Hiver make personalization easier by keeping conversation history in one place and helping agents catch up fast with AI summaries. Teams can also collaborate using internal notes and @mentions, so handoffs stay clean, and customers don’t get bounced around.
8. Leverage AI to Reduce Manual Work
When ticket volume grows, your team might start losing time to admin work: sorting requests, figuring out who should take what, and digging through long threads for context. AI can help by handling those repetitive tasks in the background, so your agents can spend more time on issues that need judgment and empathy.
Here’s how AI can help:
Auto-triage and intelligent routing
AI can read incoming messages, identify the topic and urgency, and route them to the right person based on skills and workload. That way, you don’t have to rely on managers manually assigning work or agents picking tickets on their own.
AI-generated response drafts
AI can suggest a draft response using your help content and past conversations. Your agent reviews it, edits if needed, and sends. This helps your team respond faster while keeping answers consistent.
Sentiment detection for prioritization
AI can flag messages that signal frustration or urgency so they don’t get buried in the queue. For example, if a customer says, “This is the third time I’ve followed up,” the conversation can be pushed to a higher priority so your team can step in quickly.
AI-powered knowledge bases
Unlike traditional FAQs that require customers to search and dig, AI knowledge bases understand natural language questions and pull the most relevant articles instantly. For example, when customers ask “How do I cancel my subscription?” or “What’s your return window for electronics?”, the AI can retrieve the exact answer without agent involvement.
📋Note: Most modern customer support tools now include AI to reduce manual work, like auto-tagging and routing, thread summaries, reply drafts, and basic trend reporting. The difference is how smoothly those features fit into the day-to-day workflow.
In Hiver, AI is present across the entire support cycle. AI Agents help with tagging, routing, sentiment, and capturing key details. AI Copilot supports agents with summaries and reply drafts. And AI Insights highlights repeat issues and bottlenecks, so teams can fix root causes, not just close tickets.
9. Create Accountability Systems That Build Customer Trust
Customer trust comes from reliability. That’s hard to deliver if ownership and deadlines aren’t clearly visible. You need a simple system that makes both clear.
Start by setting Service Level Agreements (SLAs) based on priority, so urgent issues get flagged fast. Add escalation triggers for cases that need fast attention, like angry sentiment, urgent keywords, or repeat follow-ups. And make ownership visible, so managers can step in early instead of finding out after the customer is already frustrated.
What to track:
- SLA breach risk: tickets close to the deadline
- Unassigned requests: tickets sitting in the queue without an owner
- Escalations: by type and by agent/team
- Repeat follow-ups: customers checking in on already-assigned tickets
💡Pro Tip: Hiver can help you set priority-based SLAs (urgent billing issues get 2-hour response targets, general how-to questions get 24 hours), and it automatically flags at-risk conversations. Managers see breach alerts before customers feel the delay.
10. Streamline Feedback Collection and Action
Feedback only helps when it leads to change. So don’t collect it randomly or only when someone complains loudly. Build a simple system that captures feedback regularly, reviews it on a schedule, and turns patterns into fixes.
Start by sending a CSAT survey after every customer interaction, so you get a consistent signal of how customers feel. Then review feedback trends monthly (and do a quick scan weekly) to spot patterns by issue type, channel, or team.
If CSAT drops for billing requests, for example, it usually means the workflow, policy, or documentation needs work, not that agents suddenly forgot how to do their jobs. Finally, close the loop by telling customers what changed based on their input. That’s how feedback turns into trust.
💡Pro Tip: Most customer support tools let you collect CSAT, but what matters is being able to break it down by issue type, agent, and time period so you know what to fix. In Hiver, you can automate CSAT after resolution and review scores by tags or categories. That makes it easier to spot patterns like “billing tickets score lower than everything else” or “refund requests lead to more follow-ups,” and then update the workflow or documentation.
Recommended reading
11. Provide Self-service Options
When customers can’t find answers on their own, they contact support for routine questions. This increases ticket volume and pulls agents away from complex issues. Self-service reduces that load by giving customers a reliable way to resolve common requests quickly, while keeping your answers consistent.
What to do:
- Start with your top recurring questions (based on ticket tags, inbox themes, and repeat conversations).
- Create short help articles with a clear lead answer, followed by step-by-step instructions.
- Link these articles in replies and chat flows so customers can self-serve next time.
- Review and update articles regularly, especially after product changes.
- Track searches and repeat tickets to identify gaps in your help content.
Pro tip: Prioritize the 10–15 topics that drive the most volume first. If you use a tool with a built-in knowledge base, such as Hiver, you can publish help articles in one place and use them consistently across channels. This also makes it easier for agents to pull the right article during replies, so customers get the same guidance every time.
Customer Service Management Examples
Customer service management is easier to understand when you see how teams apply it in real operations. The examples below show how companies use clearer ownership, structured workflows, and self-service to maintain service quality as request volume increases:
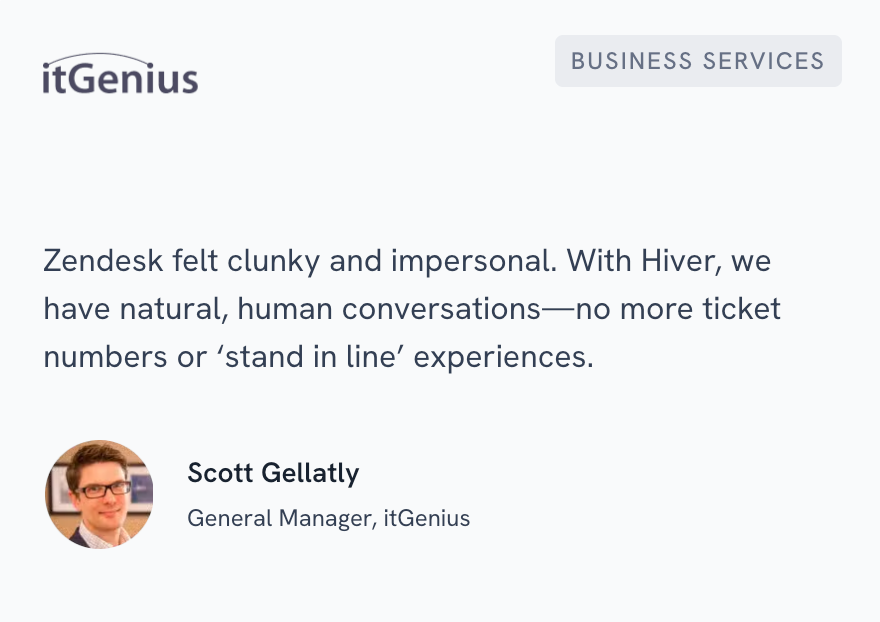
1. itGenius: Escaping Zendesk’s complexity to save 40 hours monthly
itGenius is the #1 SMB Google Cloud Partner in Australia. They were facing two major problems: they had no clear system to assign incoming emails and no visibility into who was working on what. They tried Zendesk, but the platform was expensive, clunky, and loaded with features they didn’t need.
After switching to Hiver, the team now manages 100+ daily requests using simple assignment workflows and Tags for categorization. They have complete oversight of response times and CSAT scores. The result: 40 hours saved every month and improved customer relationships.
2. Group Miki: Scaling support for 18,000+ weekly conversations
Group Miki’s Manila operations team manages hotel wholesale booking support globally. They used to handle 18,000-20,000 conversations by manually toggling between 11 shared email accounts and labeling every email by hand. This increased the average case handling time and created duplicate work.
After moving to a system with automated tagging, sentiment analysis, SLA policies, and collision alerts, case handling time dropped 67%. Moreover, 300+ automations in Hiver saved 38 hours per week.

3. Fireco: Saving 114 hours a month across multiple channels
Fireco, a fire safety solutions provider, supports customers across the UK and handles queries over email, live chat, and WhatsApp. Because these channels were disconnected, agents had to switch tools, duplicate work, and risk missing urgent requests. To meet its goals, the team switched to Hiver to centralize all three channels into a single workspace. They can now see full conversation history, route queries to specialists fast, and respond quickly to emergencies. As a result, they managed to save 114 hours per month.

Recommended reading
A Guide to Customer Service in the Information Technology (IT) Industry
Build a Customer Service Management Strategy That Scales
Support doesn’t break because teams stop caring. It breaks when volume outpaces structure. The companies that win on customer service aren’t working harder; they’re working smarter. They’ve built systems where ownership is clear, context stays intact across channels, and AI handles the busywork so agents focus on solving real problems.
Hiver is built for exactly that. It helps teams run customer service management without adding complexity. It brings customer conversations into one shared workspace, so ownership is clear, and collaboration is simple. AI also reduces manual work across the workflow, from triage and routing to summaries and reply drafts, so agents spend less time managing tickets and more time solving problems.
FAQs
1. Who is a customer service manager?
A customer service manager is the person who makes sure your support team runs smoothly. They hire and train agents, set response standards, track metrics like CSAT and resolution time, and ensure customers get consistent help no matter which channel they use. They also balance workload across your team, identify bottlenecks before they become problems, handle escalations, and turn customer feedback into actionable improvements.
2. What are the key components of customer service management?
Effective customer service management includes six core components: clear workflows with defined ownership and SLAs, omnichannel support that unifies all customer conversations in one workspace, the right tools for centralization and automation, team enablement through training and empowerment, AI-powered automation for routing and deflection, and data-driven improvement through metrics.
 Skip to content
Skip to content